Loss of the Reelin-signaling pathway differentially disrupts heat, mechanical and chemical nociceptive processing
- PMID: 22999972
- PMCID: PMC4409863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.09.027
Loss of the Reelin-signaling pathway differentially disrupts heat, mechanical and chemical nociceptive processing
Abstract
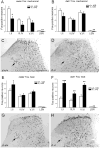
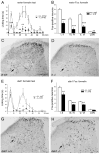
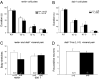
The Reelin-signaling pathway regulates neuronal positioning during embryonic development. Reelin, the extracellular matrix protein missing in reeler mutants, is secreted by neurons in laminae I, II and V, binds to Vldl and Apoer2 receptors on nearby neurons, and tyrosine phosphorylates the adaptor protein Disabled-1 (Dab1), which activates downstream signaling. We previously reported that reeler and dab1 mutants had significantly reduced mechanical and increased heat nociception. Here we extend our analysis to chemical, visceral, and cold pain and importantly, used Fos expression to relate positioning errors in mutant mouse dorsal horn to changes in neuronal activity. We found that noxious mechanical stimulation-induced Fos expression is reduced in reeler and dab1 laminae I-II, compared to wild-type mice. Additionally, mutants had fewer Fos-immunoreactive neurons in the lateral-reticulated area of the deep dorsal horn than wild-type mice, a finding that correlates with a 50% reduction and subsequent mispositioning of the large Dab1-positive cells in the mutant lateral-reticulated area. Furthermore, several of these Dab1 cells expressed Fos in wild-type mice but rarely in reeler mutants. By contrast, paralleling the behavioral observations, noxious heat stimulation evoked significantly greater Fos expression in laminae I-II of reeler and dab1 mutants. We then used the formalin test to show that chemical nociception is reduced in reeler and dab1 mutants and that there is a corresponding decrease in formalin-induced Fos expression. Finally, neither visceral pain nor cold-pain sensitivity differed between wild-type and mutant mice. As differences in the nociceptor distribution within reeler and dab1 mutant dorsal horn were not detected, these differential effects observed on distinct pain modalities suggest that dorsal horn circuits are organized along modality-specific lines.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akopians AL, Babayan AH, Beffert U, Herz J, Basbaum AI, Phelps PE. Contribution of the Reelin signaling pathways to nociceptive processing. Eur J Neuroscience. 2008;27:523–537. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud L, Ballif BA, Förster E, Cooper JA. Fyn tyrosine kinase is a critical regulator of Disabled-1 during brain development. Current Biology. 2003;13:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM, Tsuruda PR, Basbaum AI, Stucky CL, Jordt SE, Julius D. The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature. 2007;448:204–208. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Nematollah-Farsian F, Masiulis I, Hammer RE, Yoon SO, Giehl KM, Herz J. ApoE receptor 2 controls neuronal survival in the adult brain. Curr Biology. 2006;16:2446–2452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

