Cysteine-terminated B-domain of Staphylococcus aureus protein A as a scaffold for targeting GABA(A) receptors
- PMID: 23000004
- PMCID: PMC3658131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.08.031
Cysteine-terminated B-domain of Staphylococcus aureus protein A as a scaffold for targeting GABA(A) receptors
Abstract
This study reports the preparation and characterization of cysteine-terminated B-domain (Bd-cys) of Staphylococcus aureus protein A, in combination with immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies directed against the ρ1 and α1 subunits of GABA(A) receptors, for localizing reagents of interest to the target receptor. A cysteine residue was inserted at the C terminus of the cysteine-lacking B-domain (Bd) and used for conjugating maleimide-containing compounds. As determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), binding of a Bd-cys-S-fluorescein conjugate to polyclonal guinea pig anti-GABA(A)-ρ1 and rabbit anti-GABA(A)-α1 IgG was similar to that exhibited by full-length protein A. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of the interaction of Bd-cys-S-PEG3400-biotin conjugate (where PEG is polyethylene glycol) with anti-GABA(A)-ρ1 and anti-GABA(A)-α1 yielded K(D) values of 6.4 ± 1.9 and 0.4 ± 0.1 nM, respectively. Fluorescence anisotropy analysis of the binding of Bd-cys-S-fluorescein to the two antibodies yielded EC50 values of 65 and 18 nM, respectively. As determined with biotin-reactive fluorescent reagents, Bd-cys-S-PEG3400-biotin specifically bound to the plasma membrane of Xenopus laevis oocytes that expressed α1β2γ2 or homomeric ρ1 GABA(A) receptors and were pretreated with the corresponding anti-GABA(A) IgG. The IgG-binding specificity and high affinity of Bd-cys conjugates illustrate the potential of these conjugates, in combination with a selected IgG, to localize compounds of interest at specific cell surface proteins.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


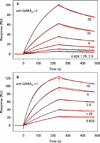


References
-
- Graille M, Stura EA, Corper AL, Sutton BJ, Taussig MJ, Charbonnier J-B, Silverman GJ. Crystal structure of a Staphylococcus aureus protein A domain complexed with the Fab fragment of a human IgM antibody: structural basis for recognition of B-cell receptors and superantigen activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000;97:5399–5404. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cedergren L, Andersson R, Jansson B, Uhlén M, Nilsson B. Mutational analysis of the interaction between staphylococcal protein A and human IgG1. Protein Eng. 1993;6:441–448. - PubMed
-
- Langone JJ. 125I-Labeled protein A: reactivity with IgG and use as a tracer in radioimmunoassay. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):356–375. - PubMed
-
- MacSween JM, Eastwood SL. Recovery of antigen from Staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbents. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73:459–471. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg UK, Jansson B, Niss U, Nilsson R, Sandberg BE, Nilsson B. The interaction between different domains of staphylococcal protein A and human polyclonal IgG, IgA, IgM, and F(ab’)2: separation of affinity from specificity. Mol. Immunol. 1993;30:1279–1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

