Reprogramming of DNA methylation in pollen guides epigenetic inheritance via small RNA
- PMID: 23000270
- PMCID: PMC3697483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.09.001
Reprogramming of DNA methylation in pollen guides epigenetic inheritance via small RNA
Abstract
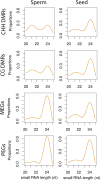
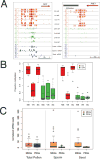
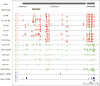
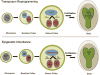
Epigenetic inheritance is more widespread in plants than in mammals, in part because mammals erase epigenetic information by germline reprogramming. We sequenced the methylome of three haploid cell types from developing pollen: the sperm cell, the vegetative cell, and their precursor, the postmeiotic microspore, and found that unlike in mammals the plant germline retains CG and CHG DNA methylation. However, CHH methylation is lost from retrotransposons in microspores and sperm cells and restored by de novo DNA methyltransferase guided by 24 nt small interfering RNA, both in the vegetative nucleus and in the embryo after fertilization. In the vegetative nucleus, CG methylation is lost from targets of DEMETER (DME), REPRESSOR OF SILENCING 1 (ROS1), and their homologs, which include imprinted loci and recurrent epialleles that accumulate corresponding small RNA and are premethylated in sperm. Thus genome reprogramming in pollen contributes to epigenetic inheritance, transposon silencing, and imprinting, guided by small RNA.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Becker C, Hagmann J, Muller J, Koenig D, Stegle O, Borgwardt K, Weigel D. Spontaneous epigenetic variation in the Arabidopsis thaliana methylome. Nature. 2011;480:245–249. - PubMed
-
- Berger F, Twell D. Germline specification and function in plants. Annu Rev. Plant Biol. 2011;62:461–484. - PubMed
-
- Boavida LC, Becker JD, Feijo JA. The making of gametes in higher plants. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49:595–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

