Crystal structure of the yeast vacuolar ATPase heterotrimeric EGC(head) peripheral stalk complex
- PMID: 23000382
- PMCID: PMC3496068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2012.08.020
Crystal structure of the yeast vacuolar ATPase heterotrimeric EGC(head) peripheral stalk complex
Abstract
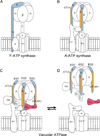
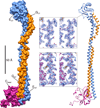
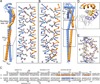
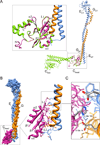
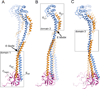
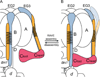
Vacuolar ATPases (V-ATPases) are multisubunit rotary motor proton pumps that function to acidify subcellular organelles in all eukaryotic organisms. V-ATPase is regulated by a unique mechanism that involves reversible dissociation into V₁-ATPase and V₀ proton channel, a process that involves breaking of protein interactions mediated by subunit C, the cytoplasmic domain of subunit "a" and three "peripheral stalks," each made of a heterodimer of E and G subunits. Here, we present crystal structures of a yeast V-ATPase heterotrimeric complex composed of EG heterodimer and the head domain of subunit C (C(head)). The structures show EG heterodimer folded in a noncanonical coiled coil that is stabilized at its N-terminal ends by binding to C(head). The coiled coil is disrupted by a bulge of partially unfolded secondary structure in subunit G and we speculate that this unique feature in the eukaryotic V-ATPase peripheral stalk may play an important role in enzyme structure and regulation by reversible dissociation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Priming a molecular motor for disassembly.Structure. 2012 Nov 7;20(11):1799-800. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.10.003. Structure. 2012. PMID: 23141690
References
-
- Alper SL. Familial renal tubular acidosis. J. Nephrol. 2010;23(Suppl 16):S57–S76. - PubMed
-
- Armbrüster A, Hohn C, Hermesdorf A, Schumacher K, Börsch M, Grüber G. Evidence for major structural changes in subunit C of the vacuolar ATPase due to nucleotide binding. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:1961–1967. - PubMed
-
- Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modeling. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Blair HC, Teitelbaum SL, Ghiselli R, Gluck S. Osteoclastic bone resorption by a polarized vacuolar proton pump. Science. 1989;245:855–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

