The flavonoid quercetin inhibits pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23000892
- PMCID: PMC3530623
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318264ccae
The flavonoid quercetin inhibits pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Objectives: The flavonoid quercetin holds promise as an antitumor agent in several preclinical animal models. However, the efficacy of oral administration of quercetin in a pancreatic cancer mouse model is unknown.
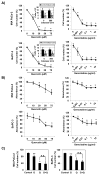
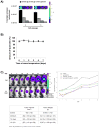
Methods: The antiproliferative effects of quercetin alone or in combination with gemcitabine were tested in 2 human pancreatic cancer cell lines using cell count and MTT assays. Apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry. Tumor growth in vivo was investigated in an orthotopic pancreatic cancer animal model using bioluminescence. Quercetin was administered orally in the diet.
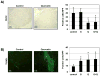
Results: Quercetin inhibited the growth of pancreatic cancer cell lines, which was caused by an induction of apoptosis. In addition, dietary supplementation of quercetin attenuated the growth of orthotopically transplanted pancreatic xenografts. The combination of gemcitabine and quercetin had no additional effect compared with quercetin alone. In vivo quercetin caused significant apoptosis and reduced tumor cell proliferation.
Conclusions: Our data provide evidence that oral administration of quercetin was capable of inhibiting growth of orthotopic pancreatic tumors in a nude mouse model. These data suggest a possible benefit of quercetin in patients with pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Thomas A, Dajani K, Neoptolemos JP, et al. Adjuvant therapy in pancreatic cancer. Dig Dis. 2010;28:684–92. - PubMed
-
- Kazanjian KK, Hines OJ, Duffy JP, et al. Improved survival following pancreaticoduodenectomy to treat adenocarcinoma of the pancreas: the influence of operative blood loss. Arch Surg. 2008;143:1166–71. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S, Wang Z, Mohammad M, et al. Efficacy of selected natural products as therapeutic agents against cancer. J Nat Prod. 2008;71:492–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

