Mutations in ADAR1 cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome associated with a type I interferon signature
- PMID: 23001123
- PMCID: PMC4154508
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2414
Mutations in ADAR1 cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome associated with a type I interferon signature
Abstract
Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) catalyze the hydrolytic deamination of adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and thereby potentially alter the information content and structure of cellular RNAs. Notably, although the overwhelming majority of such editing events occur in transcripts derived from Alu repeat elements, the biological function of non-coding RNA editing remains uncertain. Here, we show that mutations in ADAR1 (also known as ADAR) cause the autoimmune disorder Aicardi-Goutières syndrome (AGS). As in Adar1-null mice, the human disease state is associated with upregulation of interferon-stimulated genes, indicating a possible role for ADAR1 as a suppressor of type I interferon signaling. Considering recent insights derived from the study of other AGS-related proteins, we speculate that ADAR1 may limit the cytoplasmic accumulation of the dsRNA generated from genomic repetitive elements.
Figures
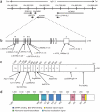
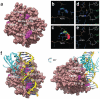
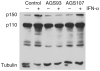
References
-
- Crow YJ, Livingston JH. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome: an important Mendelian mimic of congenital infection. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008;50:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Lebon P, et al. Intrathecal synthesis of interferon-α in infants with progressive familial encephalopathy. J. Neurol. Sci. 1988;84:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Crow YJ, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the 3′-5′ DNA exonuclease TREX1 cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome at the AGS1 locus. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:917–920. - PubMed
-
- Crow YJ, et al. Mutations in genes encoding ribonuclease H2 subunits cause Aicardi-Goutières syndrome and mimic congenital viral brain infection. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:910–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS060695/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

