Role of rpoS in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain H32 biofilm development and survival
- PMID: 23001657
- PMCID: PMC3497384
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02149-12
Role of rpoS in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain H32 biofilm development and survival
Abstract
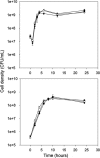
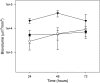
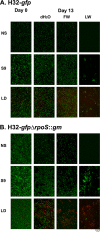
The protein RpoS is responsible for mediating cell survival during the stationary phase by conferring cell resistance to various stressors and has been linked to biofilm formation. In this study, the role of the rpoS gene in Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and survival in water was investigated. Confocal scanning laser microscopy of biofilms established on coverslips revealed a nutrient-dependent role of rpoS in biofilm formation, where the biofilm biomass volume of the rpoS mutant was 2.4- to 7.5-fold the size of its rpoS(+) wild-type counterpart in minimal growth medium. The enhanced biofilm formation of the rpoS mutant did not, however, translate to increased survival in sterile double-distilled water (ddH(2)O), filter-sterilized lake water, or unfiltered lake water. The rpoS mutant had an overall reduction of 3.10 and 5.30 log(10) in sterile ddH(2)O and filter-sterilized lake water, respectively, while only minor reductions of 0.53 and 0.61 log(10) in viable counts were observed for the wild-type form in the two media over a 13-day period, respectively. However, the survival rates of the detached biofilm-derived rpoS(+) and rpoS mutant cells were comparable. Under the competitive stress conditions of unfiltered lake water, the advantage conferred by the presence of rpoS was lost, and both the wild-type and knockout forms displayed similar declines in viable counts. These results suggest that rpoS does have an influence on both biofilm formation and survival of E. coli O157:H7 and that the advantage conferred by rpoS is contingent on the environmental conditions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phage insertion in mlrA and variations in rpoS limit curli expression and biofilm formation in Escherichia coli serotype O157: H7.Microbiology (Reading). 2013 Aug;159(Pt 8):1586-1596. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.066118-0. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Microbiology (Reading). 2013. PMID: 23744902
-
Peroxide resistance in Escherichia coli serotype O157 : H7 biofilms is regulated by both RpoS-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Microbiology (Reading). 2012 Sep;158(Pt 9):2225-2234. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.059535-0. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Microbiology (Reading). 2012. PMID: 22700652
-
Role of rpoS in acid resistance and fecal shedding of Escherichia coli O157:H7.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Feb;66(2):632-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.2.632-637.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10653728 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of rpoS and bolA genes in biofilm formation in Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Sep;342(1-2):207-13. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0485-7. Epub 2010 May 18. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20480211 Review.
-
Mechanistic and bibliometric insights into RpoS-mediated biofilm regulation and its strategic role in food safety applications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jan 29:1-15. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2458755. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39879107 Review.
Cited by
-
Escherichia coli YmdB regulates biofilm formation independently of its role as an RNase III modulator.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Nov 24;13:266. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-266. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24267348 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a better understanding of the mechanisms of symbiosis: a comprehensive proteome map of a nascent insect symbiont.PeerJ. 2017 May 9;5:e3291. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3291. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28503376 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Quinone Oxidoreductase WrbA on Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation and Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 6;10(6):919. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060919. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204135 Free PMC article.
-
The General Stress Response σS Is Regulated by a Partner Switch in the Gram-negative Bacterium Shewanella oneidensis.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 9;291(50):26151-26163. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.751933. Epub 2016 Nov 3. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27810894 Free PMC article.
-
Functional investigation of the chromosomal ccdAB and hipAB operon in Escherichia coli Nissle 1917.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Aug;104(15):6731-6747. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10733-6. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32535695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artz RR, Killham K. 2002. Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in private drinking water wells: influences of protozoan grazing and elevated copper concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 216:117–122 - PubMed
-
- Beloin C, et al. 2004. Global impact of mature biofilm lifestyle on Escherichia coli K-12 gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 51:659–674 - PubMed
-
- Bester E, Edwards EA, Wolfaardt GM. 2009. Planktonic cell yield is linked to biofilm development. Can. J. Microbiol. 55:1195–1206 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

