Histamine induces activation of protein kinase D that mediates tissue factor expression and activity in human aortic smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 23001835
- PMCID: PMC3532537
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00500.2011
Histamine induces activation of protein kinase D that mediates tissue factor expression and activity in human aortic smooth muscle cells
Abstract
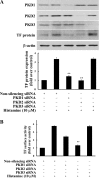
Histamine, an inflammatory mediator, has been shown to influence the pathogenesis of vascular wall cells. However, the molecular basis of its influence is not well understood. Our data reveal that histamine markedly induces protein kinase D (PKD) activation in human aortic smooth muscle cells. PKD belongs to a family of serine/threonine protein kinases, and its function in vascular disease is largely unknown. Our data show that histamine-induced PKD phosphorylation is dependent on the activation of histamine receptor 1 and protein kinase C (PKC). To determine the role of PKD in the histamine pathway, we employed a small-interfering RNA approach to downregulate PKD expression and found that PKD1 and PKD2 are key mediators for expression of tissue factor (TF), which is the key initiator of blood coagulation and is important for thrombosis. Our results show that PKD2 predominantly mediates histamine-induced TF expression via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, whereas PKD1 mediates histamine-induced TF expression through a p38 MAPK-independent pathway. We demonstrate that histamine induces TF expression via the PKC-dependent PKD activation. Our data provide the first evidence that PKD is a new component in histamine signaling in live cells and that PKD has a novel function in the histamine signaling pathway leading to gene expression, as evidenced by TF expression. Importantly, our data reveal a regulatory link from histamine to PKD and TF, providing new insights into the mechanisms of coagulation and the development of atherothrombosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LPA1-mediated PKD2 activation promotes LPA-induced tissue factor expression via the p38α and JNK2 MAPK pathways in smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Oct;297(4):101152. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101152. Epub 2021 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34478715 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin rapidly induces protein kinase D phosphorylation, and protein kinase C delta mediates the activation.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 31;278(5):2824-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211523200. Epub 2002 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12431976
-
Lysophosphatidic acid induction of tissue factor expression in aortic smooth muscle cells.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003 Feb 1;23(2):224-30. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.0000054660.61191.7d. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003. PMID: 12588763
-
Protein kinase D in vascular biology and angiogenesis.IUBMB Life. 2011 Apr;63(4):258-63. doi: 10.1002/iub.456. IUBMB Life. 2011. PMID: 21488147 Review.
-
Role of tissue factor in atherothrombosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012 Oct;14(5):394-401. doi: 10.1007/s11883-012-0269-5. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012. PMID: 22886473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential function and regulation of orphan nuclear receptor TR3 isoforms in endothelial cells.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3307-20. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4157-9. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26440050 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs in aortic dissection: From biomarkers to therapeutic targets.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(20):11622-11637. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15802. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32885591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Factors in Deep Vein Thrombosis Initiation.Trends Immunol. 2018 Aug;39(8):610-623. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.04.010. Epub 2018 May 16. Trends Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29776849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NPY/Y₁ receptor-mediated vasoconstrictory and proliferative effects in pulmonary hypertension.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;171(16):3895-907. doi: 10.1111/bph.12751. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24779394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, Deng F, Singh SV, Wang QJ. Protein kinase D3 (PKD3) contributes to prostate cancer cell growth and survival through a PKCepsilon/PKD3 pathway downstream of Akt and ERK 1/2. Cancer Res 68: 3844–3853, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Lu G, Wang QJ. Protein kinase C-independent effects of protein kinase D3 in glucose transport in L6 myotubes. Mol Pharmacol 67: 152–162, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Edwards C, Armstrong P, Goode G, Mtshali C, Williams S, Myles EL, Washington B. Cross-talking between calcium and histamine in the expression of MAPKs in hypertensive vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 53: 61–66, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

