Routine determination of GFR in renal transplant recipients by HPLC quantification of plasma iohexol concentrations and comparison with estimated GFR
- PMID: 23001984
- PMCID: PMC6807609
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21537
Routine determination of GFR in renal transplant recipients by HPLC quantification of plasma iohexol concentrations and comparison with estimated GFR
Abstract
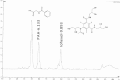
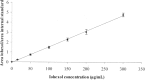
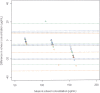
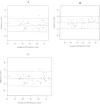
Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) methods are not sufficiently reliable in renal transplant recipients (RTR) and should be replaced by iohexol plasma clearance measurement. However, this method has poor availability in health centers. The aim of our study was to develop a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method for plasma iohexol measurement in routine practice and to evaluate its plasma clearance as a reference of GFR. We developed an HPLC method using UV detection. We evaluated sample storage conditions to provide recommendations for routine practice. Then, we compared GFRbased on plasma iohexol clearance (GFR-iohexol) to eGFR using modification of diet in renal disease, Cockcroft and Gault, and CDK-EPIequations in 40 RTR. The method was validated over a concentration range of 15-300 μg/l. Excellent linearity (r > 0.998), inter- and intraday precision (CV < 3.3%), and accuracy (>96.8%) were complied with ICH guidelines. We also demonstrated excellent samples stability (9 days). Although eGFR methods are not references in RTR, we found a correct concordance between eGFR and GFR-iohexol in our population. To conclude, our method is simple, rapid, accurate, and reliable for routine clinical and research use especially in RTR.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, et al. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med 2003;39(2):137–147. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez Ocampo J, Torres Rosales A, Rodriguez Castellanos F. Comparison of four methods for measuring glomerular filtration rate by inulin clearance in healthy individuals and patients with renal failure. Nefrologia 30(3):324–330. - PubMed
-
- Mariat C. Diagnosis and follow‐up of chronic kidney graft dysfunction: From DFG to new biomarkers. Nephrol Ther 2008;4(Suppl 3):S204–S207. - PubMed
-
- Rognant N, Bacchetta J, Dubourg L, et al. What is the best alternative to inulin clearance to estimate GFR in patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010;25(11):3569–3575. - PubMed
-
- Kooman JP. Estimation of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 2009;30(6):1341–1346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

