Animal models of Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 23002015
- PMCID: PMC3543097
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006320
Animal models of Alzheimer disease
Abstract
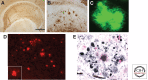
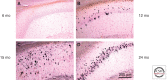
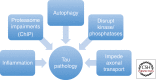
Significant insights into the function of genes associated with Alzheimer disease and related dementias have occurred through studying genetically modified animals. Although none of the existing models fully reproduces the complete spectrum of this insidious human disease, critical aspects of Alzheimer pathology and disease processes can be experimentally recapitulated. Genetically modified animal models have helped advance our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of disease and have proven to be invaluable in the preclinical evaluation of potential therapeutic interventions. Continuing refinement and evolution to yield the next generation of animal models will facilitate successes in producing greater translational concordance between preclinical studies and human clinical trials and eventually lead to the introduction of novel therapies into clinical practice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Frustrated Alzheimer's researchers seek better lab mice.Nature. 2018 Nov;563(7733):611-612. doi: 10.1038/d41586-018-07484-w. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30482928 No abstract available.
-
APP transgenic mouse models and their use in drug discovery to evaluate amyloid- lowering therapeutics.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Aug;9(4):395-402. doi: 10.2174/187152710791556087. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20522015 Review.
-
Prevention of tau increase in cerebrospinal fluid of APP transgenic mice suggests downstream effect of BACE1 inhibition.Alzheimers Dement. 2017 Jun;13(6):701-709. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Alzheimers Dement. 2017. PMID: 27750032
-
The molecular pathology of amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol. 1991;5(2-4):389-98. doi: 10.1007/BF02935560. Mol Neurobiol. 1991. PMID: 1823142 Review. No abstract available.
-
Proteolysis by presenilins and the renaissance of tau.Trends Cell Biol. 1999 Jun;9(6):241-4. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01576-7. Trends Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10408925 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The synergy of β amyloid 1-42 and oxidative stress in the development of Alzheimer's disease-like neurodegeneration of hippocampal cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 25;12(1):17883. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22761-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36284177 Free PMC article.
-
A Pathophysiological Intersection of Diabetes and Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 30;23(19):11562. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911562. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy in Two Transgenic Mouse Models of Cerebral β-Amyloidosis: A Neuropathological Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 29;23(9):4972. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094972. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563362 Free PMC article.
-
Large Animal Models of Huntington's Disease.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015;22:149-60. doi: 10.1007/7854_2013_246. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 24048953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental Pharmacology in Transgenic Rodent Models of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 4;10:189. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00189. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30886583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adlard PA, Cherny RA, Finkelstein DI, Gautier E, Robb E, Cortes M, Volitakis I, Liu X, Smith JP, Perez K, et al. 2008. Rapid restoration of cognition in Alzheimer’s transgenic mice with 8-hydroxy quinoline analogs is associated with decreased interstitial Aβ. Neuron 59: 43–55 - PubMed
-
- Billings LM, Oddo S, Green KN, McGaugh JL, LaFerla FM 2005. Intraneuronal Aβ causes the onset of early Alzheimer’s disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron 45: 675–688 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
