Zinc-finger nuclease-mediated correction of α-thalassemia in iPS cells
- PMID: 23002118
- PMCID: PMC3543982
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-420703
Zinc-finger nuclease-mediated correction of α-thalassemia in iPS cells
Abstract
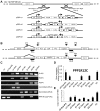
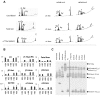
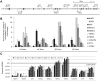
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell technology holds vast promises for a cure to the hemoglobinopathies. Constructs and methods to safely insert therapeutic genes to correct the genetic defect need to be developed. Site-specific insertion is a very attractive method for gene therapy because the risks of insertional mutagenesis are eliminated provided that a "safe harbor" is identified, and because a single set of validated constructs can be used to correct a large variety of mutations simplifying eventual clinical use. We report here the correction of α-thalassemia major hydrops fetalis in transgene-free iPS cells using zinc finger-mediated insertion of a globin transgene in the AAVS1 site on human chromosome 19. Homozygous insertion of the best of the 4 constructs tested led to complete correction of globin chain imbalance in erythroid cells differentiated from the corrected iPS cells.
Figures


References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663–676. - PubMed
-
- Hanna J, Wernig M, Markoulaki S, et al. Treatment of sickle cell anemia mouse model with iPSCs generated from autologous skin. Science. 2007;318(5858):1920–1923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

