Exercise training-enhanced, endothelium-dependent dilation mediated by altered regulation of BK(Ca) channels in collateral-dependent porcine coronary arterioles
- PMID: 23002811
- PMCID: PMC3574200
- DOI: 10.1111/micc.12016
Exercise training-enhanced, endothelium-dependent dilation mediated by altered regulation of BK(Ca) channels in collateral-dependent porcine coronary arterioles
Abstract
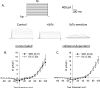
Objective: Test the hypothesis that exercise training increases the contribution of BK(Ca) channels to endothelium-mediated dilation in coronary arterioles from collateral-dependent myocardial regions of chronically occluded pig hearts and may function downstream of H2O2.
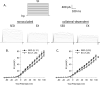
Methods: An ameroid constrictor was placed around the proximal left circumflex coronary artery to induce gradual occlusion in Yucatan miniature swine. Eight weeks postoperatively, pigs were randomly assigned to sedentary or exercise training (treadmill; 14 week) regimens.
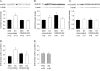
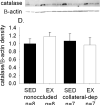
Results: Exercise training significantly enhanced bradykinin-mediated dilation in collateral-dependent arterioles (~125 μm diameter) compared with sedentary pigs. The BK(Ca) -channel blocker, iberiotoxin alone or in combination with the H2O2 scavenger, polyethylene glycol catalase, reversed exercise training-enhanced dilation in collateral-dependent arterioles. Iberiotoxin-sensitive whole-cell K+ currents (i.e., BK(Ca)-channel currents) were not different between smooth muscle cells of nonoccluded and collateral-dependent arterioles of sedentary and exercise trained groups.
Conclusions: These data provide evidence that BK(Ca)-channel activity contributes to exercise training-enhanced endothelium-dependent dilation in collateral-dependent coronary arterioles despite no change in smooth muscle BK(Ca)-channel current. Taken together, our findings suggest that a component of the bradykinin signaling pathway, which stimulates BK(Ca) channels, is enhanced by exercise training in collateral-dependent arterioles and suggest a potential role for H2O2 as the mediator.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
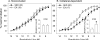
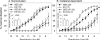
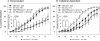
Similar articles
-
Sexually dimorphic mechanisms of H2O2-mediated dilation in porcine coronary arterioles with ischemia and endurance exercise training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Apr 1;138(4):950-963. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 40059640 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of exercise training on nitric oxide and superoxide/H₂O₂ signaling pathways in collateral-dependent porcine coronary arterioles.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 May;112(9):1546-55. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01248.2011. Epub 2012 Feb 9. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22323648 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training rescues impaired H2O2-mediated vasodilation in porcine collateral-dependent coronary arterioles through enhanced K+ channel activation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023 May 1;324(5):H637-H653. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00710.2022. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36867445 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise training on regulation of tone in coronary arteries and arterioles.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994 Oct;26(10):1252-61. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1994. PMID: 7799768 Review.
-
Regulation of coronary blood flow during exercise.Physiol Rev. 2008 Jul;88(3):1009-86. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2006. Physiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18626066 Review.
Cited by
-
Exercise training enhances multiple mechanisms of relaxation in coronary arteries from ischemic hearts.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013 Nov 1;305(9):H1321-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00531.2013. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23997097 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic mechanisms of H2O2-mediated dilation in porcine coronary arterioles with ischemia and endurance exercise training.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025 Apr 1;138(4):950-963. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 10. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2025. PMID: 40059640 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelium-Derived Hyperpolarization and Coronary Vasodilation: Diverse and Integrated Roles of Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Gap Junctions.Microcirculation. 2016 Jan;23(1):15-32. doi: 10.1111/micc.12255. Microcirculation. 2016. PMID: 26541094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myosin phosphatase isoforms and related transcripts in the pig coronary circulation and effects of exercise and chronic occlusion.Microvasc Res. 2015 Mar;98:166-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Microvasc Res. 2015. PMID: 24534069 Free PMC article.
-
H2O2-mediated relaxation in a swine model of ischemic heart disease and exercise training: mechanistic insights and the role of Kv7 channels.Basic Res Cardiol. 2025 Jul 12. doi: 10.1007/s00395-025-01129-6. Online ahead of print. Basic Res Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40650781
References
-
- Alexander B, Browse DJ, Reading SJ, Benjamin IS. A simple and accurate mathematical method for calculation of the EC50. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1999;41:55–58. - PubMed
-
- Altman JD, Kinn J, Duncker DJ, Bache RJ. Effect of inhibition of nitric oxide formation on coronary blood flow during exercise in the dog. Cardiovasc Res. 1994;28:119–124. - PubMed
-
- Barlow RS, El-Mowafy AM, White RE. H2O2 opens BKCa channels via the PLA2-arachidonic acid signaling cascade in coronary artery smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H475–H483. - PubMed
-
- Barlow RS, White RE. Hydrogen peroxide relaxes porcine coronary arteries by stimulating BKCa channel activity. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:H1283–H1289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

