Analytical model for three-dimensional Mercedes-Benz water molecules
- PMID: 23005100
- PMCID: PMC3808123
- DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.061503
Analytical model for three-dimensional Mercedes-Benz water molecules
Abstract
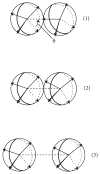
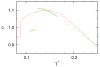
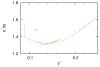
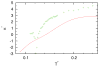
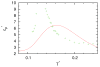
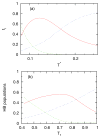
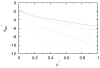
We developed a statistical model which describes the thermal and volumetric properties of water-like molecules. A molecule is presented as a three-dimensional sphere with four hydrogen-bonding arms. Each water molecule interacts with its neighboring waters through a van der Waals interaction and an orientation-dependent hydrogen-bonding interaction. This model, which is largely analytical, is a variant of a model developed before for a two-dimensional Mercedes-Benz model of water. We explored properties such as molar volume, density, heat capacity, thermal expansion coefficient, and isothermal compressibility as a function of temperature and pressure. We found that the volumetric and thermal properties follow the same trends with temperature as in real water and are in good general agreement with Monte Carlo simulations, including the density anomaly, the minimum in the isothermal compressibility, and the decreased number of hydrogen bonds upon increasing the temperature.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A statistical mechanical theory for a two-dimensional model of water.J Chem Phys. 2010 Jun 14;132(22):224507. doi: 10.1063/1.3454193. J Chem Phys. 2010. PMID: 20550408 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid critical point in a simple analytical model of water.Phys Rev E. 2016 Oct;94(4-1):042126. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.94.042126. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Phys Rev E. 2016. PMID: 27841542
-
Three-dimensional "Mercedes-Benz" model for water.J Chem Phys. 2009 Aug 7;131(5):054505. doi: 10.1063/1.3183935. J Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19673572
-
An improved thermodynamic perturbation theory for Mercedes-Benz water.J Chem Phys. 2007 Nov 7;127(17):174511. doi: 10.1063/1.2784124. J Chem Phys. 2007. PMID: 17994831
-
Theory for the three-dimensional Mercedes-Benz model of water.J Chem Phys. 2009 Nov 21;131(19):194504. doi: 10.1063/1.3259970. J Chem Phys. 2009. PMID: 19929057 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Crustwater: Modeling Hydrophobic Solvation.J Phys Chem B. 2022 Aug 18;126(32):6052-6062. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c02695. Epub 2022 Aug 4. J Phys Chem B. 2022. PMID: 35926838 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling water with simple Mercedes-Benz models.Mol Simul. 2019;45(4-5):279-294. doi: 10.1080/08927022.2018.1502430. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Mol Simul. 2019. PMID: 31156291 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical 2-Dimensional Model of Nonpolar and Ionic Solvation in Water.J Phys Chem B. 2021 Feb 25;125(7):1861-1873. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c10329. Epub 2021 Feb 4. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33539097 Free PMC article.
-
Water Is a Cagey Liquid.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Dec 12;140(49):17106-17113. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08856. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 30461279 Free PMC article.
-
How Water's Properties Are Encoded in Its Molecular Structure and Energies.Chem Rev. 2017 Oct 11;117(19):12385-12414. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00259. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28949513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Röntgen W. Ann Phys Chem. 1892;45:91.
-
- Pople JA. Proc R Soc London A. 1951;205:163.
-
- Bell GM. J Phys C. 1972;5:889.
-
- Rahman A, Stillinger FH. J Chem Phys. 1972;57:4009.
-
- Borick SS, Debenedetti PG, Sastry S. J Phys Chem. 1995;99:3781.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
