Characterization of EssB, a protein required for secretion of ESAT-6 like proteins in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 23006124
- PMCID: PMC3489787
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-219
Characterization of EssB, a protein required for secretion of ESAT-6 like proteins in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
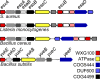
Background: Staphylococcus aureus secretes EsxA and EsxB, two small polypeptides of the WXG100 family of proteins. Genetic analyses have shown that production and secretion of EsxA and EsxB require an intact ESAT-6 Secretion System (ESS), a cluster of genes that is conserved in many Firmicutes and encompasses esxA and esxB . Here, we characterize EssB, one of the proteins encoded by the ESS cluster. EssB is highly conserved in Gram-positive bacteria and belongs to the Cluster of Orthologous Groups of protein COG4499 with no known function.
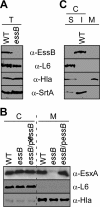
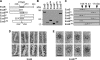
Results: By generating an internal deletion in essB , we demonstrate that EssB is required for secretion of EsxA. We use a polyclonal antibody to identify EssB and show that the protein fractionates with the plasma membrane of S. aureus . Yet, when produced in Escherichia coli, EssB remains mostly soluble and the purified protein assembles into a highly organized oligomer that can be visualized by electron microscopy. Production of truncated EssB variants in wild-type S. aureus confers a dominant negative phenotype on EsxA secretion.
Conclusions: The data presented here support the notion that EssB may oligomerize and interact with other membrane components to form the WXG100-specific translocon in S. aureus .
Figures
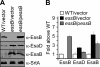

References
-
- Dalbey RE, Wickner W. Leader peptidase catalyzes the release of exported proteins from the outer surface of the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:15925–15931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

