Expression of IL-20 in synovium and lesional skin of patients with psoriatic arthritis: differential response to alefacept treatment
- PMID: 23006144
- PMCID: PMC3580512
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4038
Expression of IL-20 in synovium and lesional skin of patients with psoriatic arthritis: differential response to alefacept treatment
Abstract
Introduction: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is an inflammatory joint disease associated with psoriasis. Alefacept (a lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-3 Ig fusion protein that binds to CD2 and functions as an antagonist to T-cell activation) has been shown to result in improvement in psoriasis but has limited effectiveness in PsA. Interleukin-20 (IL-20) is a key proinflammatory cytokine involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. The effects of alefacept treatment on IL-20 expression in the synovium of patients with psoriasis and PsA are currently unknown.
Methods: Eleven patients with active PsA and chronic plaque psoriasis were treated with alefacept (7.5 mg per week for 12 weeks) in an open-label study. Skin biopsies were taken before and after 1 and 6 weeks, whereas synovial biopsies were obtained before and 4 and 12 weeks after treatment. Synovial biopsies from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 10) were used as disease controls. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to detect IL-20 expression, and stained synovial tissue sections were evaluated with digital image analysis. Double staining was performed with IL-20 and CD68 (macrophages), and conversely with CD55 (fibroblast-like synoviocytes, FLSs) to determine the phenotype of IL-20-positive cells in PsA synovium. IL-20 expression in skin sections (n = 6) was analyzed semiquantitatively.
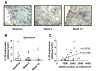
Results: IL-20 was abundantly expressed in both PsA and RA synovial tissues. In inflamed PsA synovium, CD68+ macrophages and CD55+ FLSs coexpressed IL-20, and its expression correlated with the numbers of FLSs. IL-20 expression in lesional skin of PsA patients decreased significantly (P = 0.04) 6 weeks after treatment and correlated positively with the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI). IL-20 expression in PsA synovium was not affected by alefacept.
Conclusions: Conceivably, the relatively limited effectiveness of alefacept in PsA patients (compared with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) therapy) might be explained in part by persistent FLS-derived IL-20 expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Macrophage-derived cytokine and nuclear factor kappaB p65 expression in synovial membrane and skin of patients with psoriatic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jun;43(6):1244-56. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6<1244::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-2. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10857783
-
Detailed analysis of the cell infiltrate and the expression of mediators of synovial inflammation and joint destruction in the synovium of patients with psoriatic arthritis: implications for treatment.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Dec;65(12):1551-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.050963. Epub 2006 May 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 16728461 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial features of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis in clinical and ultrasound remission differ under anti-TNF therapy: a clue to interpret different chances of relapse after clinical remission?Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jul;76(7):1228-1236. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210424. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28119289 Free PMC article.
-
Synovitis in psoriatic arthritis: immunohistochemistry, comparisons with rheumatoid arthritis, and effects of therapy.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011 Aug;13(4):353-9. doi: 10.1007/s11926-011-0181-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21503693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.BioDrugs. 2013 Jan;27 Suppl 1:3-12. doi: 10.1007/BF03325637. BioDrugs. 2013. PMID: 23990277 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukins 20 and 8 - less widely known cytokines in psoriasis.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2023 Apr;40(2):194-203. doi: 10.5114/ada.2022.119077. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2023. PMID: 37312911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution of interleukin-10 family cytokines in serum and synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis reveals different contribution to systemic and joint inflammation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2015 Feb;179(2):300-8. doi: 10.1111/cei.12449. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25178435 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Serum level of interleukin-24 and its polymorphism in eczematic Iraqi patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 21;103(25):e38635. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038635. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38905384 Free PMC article.
-
The IL-23/IL-17 axis in psoriatic arthritis.Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Apr-May;13(4-5):496-502. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.01.050. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Autoimmun Rev. 2014. PMID: 24424175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Interleukins in the Pathogenesis of Dermatological Immune-Mediated Diseases.Adv Ther. 2022 Oct;39(10):4474-4508. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02241-y. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35997892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krueger GG, Papp KA, Stough DB, Loven KH, Gulliver WP, Ellis CN. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study evaluating efficacy and tolerability of 2 courses of alefacept in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:821–833. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.127247. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kraan MC, van Kuijk AW, Dinant HJ, Goedkoop AY, Smeets TJ, de Rie MA, Dijkmans BA, Vaishnaw AK, Bos JD, Tak PP. Alefacept treatment in psoriatic arthritis: reduction of the effector T cell population in peripheral blood and synovial tissue is associated with improvement of clinical signs of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2776–2784. doi: 10.1002/art.10543. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

