Serum TGF-β, Serum MMP-1, and HOMA-IR as non-invasive predictors of fibrosis in Egyptian patients with NAFLD
- PMID: 23006461
- PMCID: PMC3500022
- DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.101132
Serum TGF-β, Serum MMP-1, and HOMA-IR as non-invasive predictors of fibrosis in Egyptian patients with NAFLD
Abstract
Background/aim: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an increasingly prevalent cause of chronic liver disease worldwide. A number of these patients progress to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) which carries significant morbidity and mortality. The aim of this study is to evaluate the diagnostic value of serum levels of transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1) matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), and insulin resistance as predictors of fibrosis in Egyptian NAFLD patients.
Patients and methods: Fifty patients with NAFLD and different stages of fibrosis were studied. Serum levels of TGF-β1, MMP-1, and fasting serum insulin were measured; calculation of the homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was done.
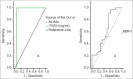
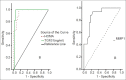
Results: TGF-β1 gives a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 94.4% for stage 1 fibrosis, 100% and 93.9%, respectively, for stage 2 fibrosis, and 97.7% and 100%, respectively, for stage 3 fibrosis. MMP-1 showed sensitivity and specificity of 88% and 81.8%, respectively, for stage 2 fibrosis, 90.9% and 55.56%, respectively, for stage 3 fibrosis, but it is of no diagnostic value in stage 1 fibrosis.
Conclusion: Serum TGF-β1, MMP-1, and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) proved to be potentially useful noninvasive markers in predicting fibrosis in NASH patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1898–906. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–21. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Sanderson S, Lindor KD. The histological course of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A longitudinal study of 103 patients with sequential liver biopsies. J Hepatol. 2005;42:132–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical