Electronic monitoring of symptoms and syndromes associated with cancer: methods of a randomized controlled trial SAKK 95/06 E-MOSAIC
- PMID: 23006802
- PMCID: PMC3517324
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-684X-11-19
Electronic monitoring of symptoms and syndromes associated with cancer: methods of a randomized controlled trial SAKK 95/06 E-MOSAIC
Abstract
Background: In patients with advanced, incurable cancer, anticancer treatment may be used to alleviate cancer-related symptoms, but monitoring of them in daily practice is rarely done. We aim to test the effectiveness of a real-time symptom and syndrome assessment using the E-MOSAIC software installed in handheld computer generating a longitudinal monitoring sheet (LoMoS) provided to the oncologists in a phase III setting.
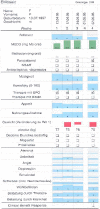
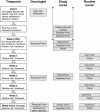
Methods: In this prospective multicentre cluster randomized phase-III trial patients with any incurable solid tumor and having defined cancer related symptoms, who receive new outpatient chemotherapy in palliative intention (expected tumor-size response rate ≤20%) are eligible. Immediately before the weekly visit to oncologists, all patients complete with nurse assistance the E-MOSAIC Assessment: Edmonton Symptom Assessment Scale, ≤3 additional symptoms, estimated nutritional intake, body weight, Karnofsky and medications for pain and cachexia. Experienced oncologists will be randomized to receive the LoMoS or not. To minimize contamination, LoMoS are removed from the medical charts after visits. Primary endpoint is the difference in global quality of life (items 29 & 30 of EORTC-QlQ-C30) between baseline and last study visit at week 6, with a 10 point between-arm difference considered to be clinically relevant. 20 clusters (=oncologists) per treatment arm with 4-8 patients each are aimed for to achieve a significance level of 5% and a power of 80% in a mixed model approach. Selected co- variables are included in the model for adjustment. Secondary endpoints include patient-perceived patient-physician communication symptom burden over time, and oncologists' symptom management performance (predefined thresholds of symptoms compared to oncologists' pharmacological, diagnostic or counselling actions [structured chart review]).
Discussion: This trial will contribute to the research question, whether structured, longitudinal monitoring of patients' multidimensional symptoms, indicators for symptom management, and clinical benefit outcomes can influence patients' quality of life and symptom distress, in a setting of routine oncology practice.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials NCT00477919.
Figures
References
-
- Doyle C, Crump M, Pintilie M, Oza AM. Does palliative chemotherapy palliate? Evaluation of expectations, outcomes, and costs in women receiving chemotherapy for advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(11230467):1266–1274. - PubMed
-
- Michael M, Hedley D, Oza A, Feld R, Pintilie M, Goel R, Maroun J, Jolivet J, Fields A, Lee IM. et al. The palliative benefit of irinotecan in 5-fluorouracil-refractory colorectal cancer: its prospective evaluation by a Multicenter Canadian Trial. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2002;2(2):93–101. doi: 10.3816/CCC.2002.n.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Adak S, Cella D, DeVore RF, Johnson DH. Topotecan versus observation after cisplatin plus etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: E7593–a phase III trial of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(11304763):2114–2122. - PubMed
-
- Passik SD, Kirsh KL. The importance of quality-of-life endpoints in clinical trials to the practicing oncologist. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14(10949778):877–886. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical