Regulation of tissue factor coagulant activity on cell surfaces
- PMID: 23006890
- PMCID: PMC3558600
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.12003
Regulation of tissue factor coagulant activity on cell surfaces
Abstract
Tissue factor (TF) is a transmembrane glycoprotein and an essential component of the factor VIIa-TF enzymatic complex that triggers activation of the coagulation cascade. Formation of TF-FVIIa complexes on cell surfaces not only trigger the coagulation cascade but also transduce cell signaling via activation of protease-activated receptors. Tissue factor is expressed constitutively on cell surfaces of a variety of extravascular cell types, including fibroblasts and pericytes in and surrounding blood vessel walls and epithelial cells, but is generally absent on cells that come into contact with blood directly. However, TF expression could be induced in some blood cells, such as monocytes and endothelial cells, following an injury or pathological stimuli. Tissue factor is essential for hemostasis, but aberrant expression of TF leads to thrombosis. Therefore, a proper regulation of TF activity is critical for the maintenance of hemostatic balance and health in general. TF-FVIIa coagulant activity at the cell surface is influenced not only by TF protein expression levels but also independently by a variety of mechanisms, including alterations in membrane phospholipid composition and cholesterol content, thiol-dependent modifications of TF allosteric disulfide bonds, and other post-translational modifications of TF. In this article, we critically review the key literature on mechanisms by which TF coagulant activity is regulated at the cell surface in the absence of changes in TF protein levels with specific emphasis on recently published data and provide the authors' perspective on the subject.
Keywords: cholesterol; cryptic; decryption; encryption; factor VIIa; glycosylation; phospholipids; protein disulfide isomerase; tissue factor.
© 2012 International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
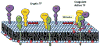


References
-
- Fleck RA, Rao LVM, Rapaport SI, Varki N. Localization of human tissue factor antigen by immunostaining with monospecific, polyclonal anti-human tissue factor antibody. Thromb Res. 1990;59:421–37. - PubMed
-
- Contrino J, Hair G, Kreutzer DL, Rickles FR. In situ detection of tissue factor in vascular endothelial cells: Correlation with the malignant phenotype of human breast disease. Nature Medicine. 1996;2:209–15. - PubMed
-
- Osterud B, Flaegstad T. Increased thromboplastin activity in monocytes of patients with meningococcal infection: Related to an unfavorable prognosis. Thromb Haemost. 1983;49:5–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

