Factors regulated by interferon gamma and hypoxia-inducible factor 1A contribute to responses that protect mice from Coccidioides immitis infection
- PMID: 23006927
- PMCID: PMC3528620
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-218
Factors regulated by interferon gamma and hypoxia-inducible factor 1A contribute to responses that protect mice from Coccidioides immitis infection
Abstract
Background: Coccidioidomycosis results from airborne infections caused by either Coccidioides immitis or C. posadasii. Both are pathogenic fungi that live in desert soil in the New World and can infect normal hosts, but most infections are self-limited. Disseminated infections occur in approximately 5% of cases and may prove fatal. Mouse models of the disease have identified strains that are resistant (e.g. DBA/2) or susceptible (e.g. C57BL/6) to these pathogens. However, the genetic and immunological basis for this difference has not been fully characterized.
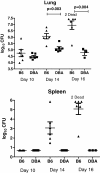
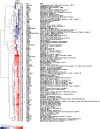
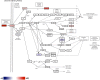
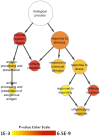
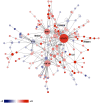
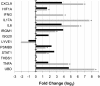
Results: Microarray technology was used to identify genes that were differentially expressed in lung tissue between resistant DBA/2 and sensitive C57BL/6 mice after infection with C. immitis. Differentially expressed genes were mapped onto biological pathways, gene ontologies, and protein interaction networks, which revealed that innate immune responses mediated by Type II interferon (i.e., IFNG) and the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) contribute to the resistant phenotype. In addition, upregulation of hypoxia inducible factor 1A (HIF1A), possibly as part of a larger inflammatory response mediated by tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFA), may also contribute to resistance. Microarray gene expression was confirmed by real-time quantitative PCR for a subset of 12 genes, which revealed that IFNG HIF1A and TNFA, among others, were significantly differentially expressed between the two strains at day 14 post-infection.
Conclusion: These results confirm the finding that DBA/2 mice express more Type II interferon and interferon stimulated genes than genetically susceptible strains and suggest that differential expression of HIF1A may also play a role in protection.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

