Paneth cells and necrotizing enterocolitis: a novel hypothesis for disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 23006982
- PMCID: PMC3609425
- DOI: 10.1159/000342340
Paneth cells and necrotizing enterocolitis: a novel hypothesis for disease pathogenesis
Abstract
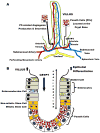
Current models of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) propose that intraluminal microbes destroy intestinal mucosa and activate an inflammatory cascade that ends in necrosis. We suggest an alternate hypothesis wherein NEC is caused by injury to Paneth cells (PCs) in the intestinal crypts. PCs are specialized epithelia that protect intestinal stem cells from pathogens, stimulate stem cell differentiation, shape the intestinal microbiota, and assist in repairing the gut. Our novel model of NEC uses neonatal mice and ablates PCs followed by enteral infection. We contrast this model with other animal examples of NEC and the clinical disease. Selective destruction of PCs using dithizone likely releases tumor necrosis factor-α and other inflammatory mediators. We propose that this event produces inflammation in the submucosa, generates platelet-activating factor, and induces a coagulopathy. The role of PCs in NEC is consistent with the onset of disease in preterm infants after a period of PC-related maturation, the central role of PCs in crypt-related homeostasis, the anatomic location of pneumatosis intestinalis close to the crypts, and the proximity of PCs to occluded blood vessels that cause coagulation necrosis of the intestinal villi. We offer this hypothesis to promote new thoughts about how NEC occurs and its potential prevention.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. McElroy, Underwood and Sherman have no financial conflicts of interest to report.
Figures



References
-
- Kliegman RM, Fanaroff AA. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:1093–1103. - PubMed
-
- Hsueh W, De Plaen IG, Caplan MS, Qu XW, Tan XD, Gonzalez-Crussi F. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: clinical aspects, experimental models and pathogenesis. World J Pediatr. 2007;3:17–29.
-
- Grave GD, Nelson SA, Walker WA, Moss RL, Dvorak B, Hamilton FA, Higgins R, Raju TN. New therapies and preventive approaches for necrotizing enterocolitis: report of a research planning workshop. Pediatr Res. 2007;62:510–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

