Proteome variation among Filifactor alocis strains
- PMID: 23008013
- PMCID: PMC4514522
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201200211
Proteome variation among Filifactor alocis strains
Abstract
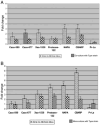
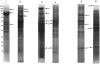
Filifactor alocis, a Gram-positive anaerobic rod, is now considered one of the marker organisms associated with periodontal disease. Although there was heterogeneity in its virulence potential, this bacterium was shown to have virulence properties that may enhance its ability to survive and persist in the periodontal pocket. To gain further insight into a possible mechanism(s) of pathogenesis, the proteome of F. alocis strains was evaluated. Proteins including several proteases, neutrophil-activating protein A and calcium-binding acid repeat protein, were identified in F. alocis. During the invasion of HeLa cells, there was increased expression of several of the genes encoding these proteins in the potentially more virulent F. alocis D-62D compared to F. alocis ATCC 35896, the type strain. A comparative protein in silico analysis of the proteome revealed more cell wall anchoring proteins in the F. alocis D-62D compared to F. alocis ATCC 35896. Their expression was enhanced by coinfection with Porphyromonas gingivalis. Taken together, the variation in the pathogenic potential of the F. alocis strains may be related to the differential expression of several putative virulence factors.
© 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Saito A, Inagaki S, Kimizuka R, Okuda K, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum enhances invasion of human gingival epithelial and aortic endothelial cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008;54:349–355. - PubMed
-
- Saito A, Inagaki S, Ishihara K. Differential ability of periodontopathic bacteria to modulate invasion of human gingival epithelial cells by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Microb Pathog. 2009;47:329–333. - PubMed
-
- Amano A. Disruption of epithelial barrier and impairment of cellular function by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Front Biosci. 2007;12:3965–3974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

