In vitro and In vivo characterization of the transdermal delivery of sertraline hydrochloride Films
- PMID: 23008688
- PMCID: PMC3436079
In vitro and In vivo characterization of the transdermal delivery of sertraline hydrochloride Films
Abstract
Background and the purpose of the study: Sertraline hydrochloride is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor principally used in the treatment of major depressive disorder. To maintain the therapeutic plasma drug concentration of the drug for prolonged period, the transdermal drug delivery has been chosen as an alternative route of drug delivery. The pharmacokinetic properties of sertraline hydrochloride make it suitable for transdermal delivery. The purpose of the study was to investigate the effect of polymers and penetration enhancers on the transdermal delivery of the drug in order to improve its therapeutic efficacy.
Methods: In the preparation of films, Eudragit RL 100, Eudragit RS 100, hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) and ethyl cellulose were used as polymers. The films were characterized for thickness, tensile strength, drug content, moisture uptake, moisture content, water vapor transmission rate and drug release. The films exhibiting higher rates of drug release were subjected to study the effect of oleic acid and propylene glycol as penetration enhancers on skin permeation of sertraline hydrochloride. In vivo and skin irritation studies were performed for the optimized film.
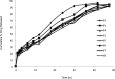
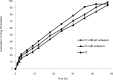
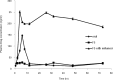
Results: Films containing Eudragit RL 100, Eudragit RL 100 and HPMC showed the highest drug release of 94.34% and 96.90% respectively in a period of 42 hrs. The release data fitted into kinetic equations, yielded zero-order and fickian mechanism of drug release. There was a two-fold increase in skin permeation of sertraline hydrochloride in the presence of penetration enhancers in the film. The physical evaluation indicated the formation of smooth, flexible and translucent films. No skin irritation occurred on rabbit skin and the infrared studies showed the compatibility of the drug with the formulation excipients. The in vivo study revealed a constant plasma concentration of drug for long periods and the films containing penetration enhancers had achieved adequate plasma levels of the drug.
Conclusions: The obtained results indicated the feasibility for transdermal delivery of sertraline hydrochloride using eudragit RL 100 and HPMC.
Keywords: Antidepressant; Ethyl Cellulose; Eudragit; Hydroxy Propyl Methyl Cellulose; In-Vitro and In-Vivo Skin Permeation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Formulation of Polymers-Based Methotrexate Patches and Investigation of the Effect of Various Penetration Enhancers: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Characterization.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 30;14(11):2211. doi: 10.3390/polym14112211. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683883 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Component Excipients on the Quality and Functionality of a Transdermal Film Formulation.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Dec;16(6):1344-56. doi: 10.1208/s12249-015-0322-0. Epub 2015 Apr 29. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25922089 Free PMC article.
-
Development of matrix type transdermal patches of lercanidipine hydrochloride: physicochemical and in-vitro characterization.Daru. 2010;18(1):9-16. Daru. 2010. PMID: 22615587 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and evaluation of diltiazem hydrochloride diffusion-controlled transdermal delivery system.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(2):464-70. doi: 10.1208/s12249-008-9062-8. Epub 2008 Mar 14. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008. PMID: 18431661 Free PMC article.
-
PREPARATION, IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF HYDROPHOBIC PATCHES OF A HIGHLY WATER SOLUBLE DRUG FOR PROLONGED PLASMA HALF LIFE: EFFECT OF PERMEATION ENHANCERS.Acta Pol Pharm. 2016 Nov;73(6):1639-1648. Acta Pol Pharm. 2016. PMID: 29634120
Cited by
-
Transfersomes: a novel vesicular carrier for enhanced transdermal delivery of sertraline: development, characterization, and performance evaluation.Sci Pharm. 2012 Oct-Dec;80(4):1061-80. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1208-02. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Sci Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23264950 Free PMC article.
-
An Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid as a Model to Study Plasticization Effects on Cationic Polymethacrylate Films.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Feb 28;15(5):1239. doi: 10.3390/polym15051239. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904480 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System Derived Tablet Containing Sertraline.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 31;14(2):336. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020336. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hollister LE. Norwalk, Connecticut: Appleton & Lange; 1995. A Lange Medical Book: Basic and Clinical Pharmacology; pp. 448–59.
-
- Kilts CD. Potential New Drug Delivery Systems for Antidepressants: An overview. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64:31–3. - PubMed
-
- Frampton JE, Plosker GL. Selegiline transdermal system: in the treatment of major depressive disorder: Profile report. CNS Drugs. 2007;21:521–24. - PubMed
-
- Mutalik S, Udupa N. Glibenclamide transdermal patches: physicochemical, pharmacodynamic, and pharmacokinetic evaluations. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93:1577–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
