Identification and characterization of potential impurities in raloxifene hydrochloride
- PMID: 23008809
- PMCID: PMC3447609
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1204-13
Identification and characterization of potential impurities in raloxifene hydrochloride
Abstract
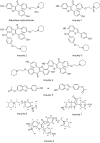
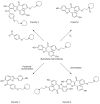
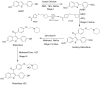
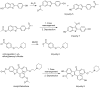
During the synthesis of the bulk drug Raloxifene hydrochloride, eight impurities were observed, four of which were found to be new. All of the impurities were detected using the gradient high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method, whose area percentages ranged from 0.05 to 0.1%. LCMS was performed to identify the mass number of these impurities, and a systematic study was carried out to characterize them. These impurities were synthesized and characterized by spectral data, subjected to co-injection in HPLC, and were found to be matching with the impurities present in the sample. Based on their spectral data (IR, NMR, and Mass), these impurities were characterized as Raloxifene-N-Oxide [Impurity: 1]; EP impurity A [Impurity: 2]; EP impurity B [Impurity: 3]; Raloxifene Dimer [Impurity: 4]; HABT (6-Acetoxy-2-[4-hydroxyphenyl]-1-benzothiophene or 6-Hydroxy-2-[4-acetoxyphenyl]-1-benzothiophene) [Impurity: 5]; PEBE (Methyl[4-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy]]benzoate) [Impurity: 6]; HHBA (1-[6-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-benzothiophen-3-yl]ethanone) [Impurity: 7]; 7-MARLF (7-Acetyl-[6-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-benzothiophen-3-yl][4-[2-(piperidin-1-yl)ethoxy]phenyl methanone) [Impurity: 8]; of which impurities 5-8 are reported for the first time.
Keywords: Characterization; Evista; Impurities; Isolation; Preparative high performance liquid chromatography; Raloxifene; Synthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Grese TA, Dodge JA. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) Curr Pharm Des. 1998;4:71–92. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10197034. - PubMed
-
- Bryant HU, Dere WH. Selective estrogen receptor modulators: an alternative to hormone replacement therapy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1998;217:45–52. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9421206. - PubMed
-
- Jones CD, Jevikar MG, Pike AJ, Peters MK, Black LJ, Thompson AR, Falcone JF, Clemens JA. Antiestrogens. 2: Structure activity studies in a series of 3-aroyl-2-arylbenzo[b]thiophene derivatives leading to [6-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)benzo[b]thien-3-yl][4-[2-(1-piperidinyl)ethoxy]-phenyl] methanone hydrochloride (LY156758), a remarkably effective estrogen antagonist with only minimal intrinsic estro-genicity. J Med Chem. 1984;27:1057–1066. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm00374a021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sato M, Grese TA, Dodge JA, Bryant HU, Turner CH. Emerging therapies for the prevention or treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Med Chem. 1999;42:1–24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm980344o. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Draper MW, Flowers DE, Huster WJ, Neild JA, Harper KD, Arnaud CJ. A controlled trial of raloxifene (LY139481) HCl: Impact on bone turnover and serum lipid profile in healthy postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 1996;11:835–842. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.5650110615. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources