Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP: do overlap cases exist?
- PMID: 23009177
- PMCID: PMC3517389
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1172-7-72
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, DRESS, AGEP: do overlap cases exist?
Abstract
Background: Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs (SCARs) include acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and epidermal necrolysis (Stevens-Johnson syndrome-toxic epidermal necrolysis [SJS-TEN]). Because of the varied initial presentation of such adverse drug reactions, diagnosis may be difficult and suggests overlap among SCARs. Overlapping SCARs are defined as cases fulfilling the criteria for definite or probable diagnosis of at least 2 ADRs according to scoring systems for AGEP, DRESS and SJS-TEN. We aimed to evaluate the prevalence of overlap among SCARs among cases in the referral hospital in France.
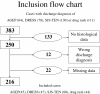
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data for 216 patients hospitalized in the referral centre over 7 years with a discharge diagnosis of AGEP (n = 45), DRESS (n = 47), SJS-TEN (n = 80) or "drug rash" (n = 44). Each case with detailed clinical data and a skin biopsy specimen was scored for AGEP, DRESS and SJS-TEN by use of diagnostic scores elaborated by the RegiSCAR group.
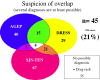
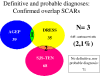
Results: In total, 45 of 216 cases (21%) had at least 2 possible diagnoses: 35 had a single predominant diagnosis (definite or probable), 7 had several possible diagnoses and 3 (2.1% of 145 confirmed SCARs) were overlap SCARs.
Conclusions: Despite ambiguities among SCARs, confirmed overlap cases are rare. This study did not avoid pitfalls linked to its retrospective nature and selection bias. In the acute stage of disease, early identification of severe ADRs can be difficult because of clinical or biologic overlapping features and missing data on histology, biology and evolution. Retrospectively analyzing cases by use of diagnostic algorithms can lead to reliable discrimination among AGEP, DRESS and SJS-TEN.
Figures
References
-
- Wolf R, Orion E, Marcos B, Matz H. Life-threatening acute adverse cutaneous drug reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2005;23(2):171–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources