Contrasting habitat associations of imperilled endemic stream fishes from a global biodiversity hot spot
- PMID: 23009367
- PMCID: PMC3528430
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6785-12-19
Contrasting habitat associations of imperilled endemic stream fishes from a global biodiversity hot spot
Abstract
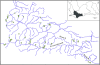
Background: Knowledge of the factors that drive species distributions provides a fundamental baseline for several areas of research including biogeography, phylogeography and biodiversity conservation. Data from 148 minimally disturbed sites across a large drainage system in the Cape Floristic Region of South Africa were used to test the hypothesis that stream fishes have similar responses to environmental determinants of species distribution. Two complementary statistical approaches, boosted regression trees and hierarchical partitioning, were used to model the responses of four fish species to 11 environmental predictors, and to quantify the independent explanatory power of each predictor.
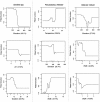
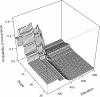
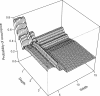
Results: Elevation, slope, stream size, depth and water temperature were identified by both approaches as the most important causal factors for the spatial distribution of the fishes. However, the species showed marked differences in their responses to these environmental variables. Elevation and slope were of primary importance for the laterally compressed Sandelia spp. which had an upstream boundary below 430 m above sea level. The fusiform shaped Pseudobarbus 'Breede' was strongly influenced by stream width and water temperature. The small anguilliform shaped Galaxias 'nebula' was more sensitive to stream size and depth, and also penetrated into reaches at higher elevation than Sandelia spp. and Pseudobarbus 'Breede'.
Conclusions: The hypothesis that stream fishes have a common response to environmental descriptors is rejected. The contrasting habitat associations of stream fishes considered in this study could be a reflection of their morphological divergence which may allow them to exploit specific habitats that differ in their environmental stressors. Findings of this study encourage wider application of complementary methods in ecological studies, as they provide more confidence and deeper insights into the variables that should be managed to achieve desired conservation outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata Z-I, Knowler DJ, Lévêque C, Naiman NJ, Prieur-Richard A-H, Soto D, Stiassny MLJ, Sullivan CA. Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol Rev. 2006;81:163–182. - PubMed
-
- Holland RA, Darwaal WRT, Smith KG. Conservation priorities for freshwater biodiversity: The Key Biodiversity Area approach refined and tested for continental Africa. Biol Conserv. 2012;148:167–179. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2012.01.016. - DOI
-
- Thacker CE, Unmack PJ, Matsui L, Rifenbark N. Comparative phylogeography of five sympatric Hypseleotris species (Teleostei: Eleotridae) in south-eastern Australia reveals a complex pattern of drainage basin exchanges with little congruence across species. J Biogeogr. 2007;34:1518–1533. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01711.x. - DOI
-
- Guisan A, Zimmerman NE. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol Model. 2000;135:147–186. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00354-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

