The bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs signatures differentially expressed in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers
- PMID: 23009584
- PMCID: PMC3545315
- DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2012.1311
The bioinformatics analysis of miRNAs signatures differentially expressed in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers
Abstract
Objective: To identify the signatures of miRNAs differentially expressed in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers that accurately predict the HER2 status of breast cancer, and to provide further insight into breast cancer therapy.
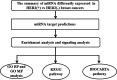
Methods: By the methods of literature search, aberrant expressed miRNAs were collected. By target prediction algorithm of TargetScan and PicTar and the data enrichment analysis, target gene sets of miRNAs differentially expressed in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers were built. Then, using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) database, the function modules of Gene Ontology categories and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and BIOCARTA pathway, biological functions and signaling pathways that are probably regulated by miRNAs, were analyzed.
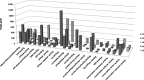
Results: We got five sets of miRNAs expressed in different HER2 status of breast cancers finally. The five sets of data contain 22; 32; 3; 38; and 62 miRNAs, respectively. After miRNAs target prediction and data enrichment, 5,734; 22,409; 1,142; 22,293; and 43,460 target genes of five miRNA sets were collected. Gene ontology analysis found these genes may be involved in transcription, protein transport, angiogenesis, and apoptosis. Moreover, certain KEGG and BIOCARTA signaling pathways related toHER2 status were found.
Conclusion: Using TargetScan and PicTar for data enrichment, and DAVID database, Gene Ontology categories, KEGG and BIOCARTA pathway for analysis of miRNAs different expression, we conducted a new method for biological interpretation of miRNA profiling data in HER2(+) versus HER2(-) breast cancers. It may improve understanding the regulatory roles of miRNAs in different molecular subtypes of breast cancers. Therefore, it is beneficial to improve the accuracy of experimental efforts to breast cancer and potential therapeutic targets.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analysis of regulated MicroRNAs by placental growth factor signaling in cancer stem cells.J Cancer Res Ther. 2020 Dec;16(Supplement):S90-S94. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_316_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33380659
-
Target genes prediction and functional analysis of microRNAs differentially expressed in gastric cancer stem cells MKN-45.J Cancer Res Ther. 2017 Jul-Sep;13(3):477-483. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.213691. J Cancer Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28862212
-
Identification of key microRNAs and hub genes in non-small-cell lung cancer using integrative bioinformatics and functional analyses.J Cell Biochem. 2020 Mar;121(3):2690-2703. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29489. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31692035
-
Computational methods for analysis of cellular functions and pathways collectively targeted by differentially expressed microRNA.Methods. 2008 Jan;44(1):61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.10.005. Methods. 2008. PMID: 18158134 Review.
-
Systematic enrichment analysis of microRNA expression profiling studies in endometriosis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 May;18(5):423-9. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26124927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-509 suppresses brain metastasis of breast cancer cells by modulating RhoC and TNF-α.Oncogene. 2015 Sep 10;34(37):4890-900. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.412. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25659578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of manimal miRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350. - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A. Slack FJ. Oncomirs—miRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259. - PubMed
-
- Calin GA. Croce CM. MiRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R. Ward E. Brawley O. Jemal A. The impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

