ESTclean: a cleaning tool for next-gen transcriptome shotgun sequencing
- PMID: 23009593
- PMCID: PMC3630001
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-247
ESTclean: a cleaning tool for next-gen transcriptome shotgun sequencing
Abstract
Background: With the advent of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, full cDNA shotgun sequencing has become a major approach in the study of transcriptomes, and several different protocols in 454 sequencing have been invented. As each protocol uses its own short DNA tags or adapters attached to the ends of cDNA fragments for labeling or sequencing, different contaminants may lead to mis-assembly and inaccurate sequence products.
Results: We have designed and implemented a new program for raw sequence cleaning in a graphical user interface and a batch script. The cleaning process consists of several modules including barcode trimming, sequencing adapter trimming, amplification primer trimming, poly-A tail trimming, vector screening and low quality region trimming. These modules can be combined based on various sequencing applications.
Conclusions: ESTclean is a software package not only for cleaning cDNA sequences, but also for helping to develop sequencing protocols by providing summary tables and figures for sequencing quality control in a graphical user interface. It outperforms in cleaning read sequences from complicated sequencing protocols which use barcodes and multiple amplification primers.
Figures

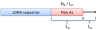





Similar articles
-
Skewer: a fast and accurate adapter trimmer for next-generation sequencing paired-end reads.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014 Jun 12;15:182. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-182. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24925680 Free PMC article.
-
ClinQC: a tool for quality control and cleaning of Sanger and NGS data in clinical research.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Feb 2;17:56. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0915-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26830926 Free PMC article.
-
Btrim: a fast, lightweight adapter and quality trimming program for next-generation sequencing technologies.Genomics. 2011 Aug;98(2):152-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.05.009. Epub 2011 May 30. Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21651976
-
EasyQC: Tool with Interactive User Interface for Efficient Next-Generation Sequencing Data Quality Control.J Comput Biol. 2018 Dec;25(12):1301-1311. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2017.0186. Epub 2018 Sep 8. J Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 30204482
-
Library preparation methods for next-generation sequencing: tone down the bias.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Mar 10;322(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24440557 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary divergence of core and post-translational circadian clock genes in the pitcher-plant mosquito, Wyeomyia smithii.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 6;16:754. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1937-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26444857 Free PMC article.
-
SeqControl: process control for DNA sequencing.Nat Methods. 2014 Oct;11(10):1071-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3094. Epub 2014 Aug 31. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 25173705
References
-
- Cross_match. http://www.phrap.org/phredphrapconsed.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

