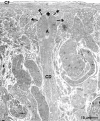
Illustration of extensive extracellular matrix at the epithelial-mesenchymal interface within the renal stem/progenitor cell niche
- PMID: 23009620
- PMCID: PMC3511299
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6890-12-16
Illustration of extensive extracellular matrix at the epithelial-mesenchymal interface within the renal stem/progenitor cell niche
Abstract
Background: Stem/progenitor cells are promising candidates to treat diseased renal parenchyma. However, implanted stem/progenitor cells are exposed to a harmful atmosphere of degenerating parenchyma. To minimize hampering effects after an implantation investigations are in progress to administer these cells within an artificial polyester interstitum supporting survival. Learning from nature the renal stem/progenitor cell niche appears as a valuable model. At this site epithelial stem/progenitor cells within the collecting duct ampulla face mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells. Both cell types do not have close contact but are separated by a wide interstitium.
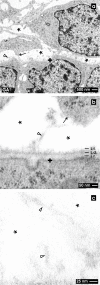
Methods: To analyze extracellular matrix in this particular interstitium, special contrasting for transmission electron microscopy was performed. Kidneys of neonatal rabbits were fixed in solutions containing glutaraldehyde (GA) or in combination with cupromeronic blue, ruthenium red and tannic acid.
Results: GA revealed a basal lamina at the ampulla and a bright but inconspicuously looking interstitial space. In contrast, GA containing cupromeronic blue exhibits numerous proteoglycan braces lining from the ampulla towards the interstitial space. GA containing ruthenium red or tannic acid demonstrates clouds of extracellular matrix protruding from the basal lamina of the ampulla to the surface of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells.
Conclusions: The actual data show that the interstitium between epithelial and mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells contains much more and up to date unknown extracellular matrix than earlier observed by classical GA fixation.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

