Therapy with JAK2 inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms
- PMID: 23009939
- PMCID: PMC4406395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hoc.2012.07.008
Therapy with JAK2 inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms
Abstract
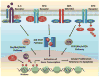
The development of JAK2 inhibitors followed the discovery of activating mutation of JAK2 (JAK2V617F) in patients with classic Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (Ph-negative MPN). It is now known that mutations activating the JAK-STAT pathway are ubiquitous in Ph-negative MPN, and that the deregulated JAK-STAT pathway plays a central role in the pathogenesis of these disorders. JAK2 inhibitors thus are effective in patients both with and without the JAK2V617F mutation. This article reviews the rationale for using JAK2 inhibitors in Ph-negative MPN, and the results of more recent clinical trials with these drugs.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
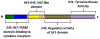
References
-
- Thiele J, Kvasnicka HM, Tefferi A, et al. Primary Myelofibrosis. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al., editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008. pp. 44–47.
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365:1054–61. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–8. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1779–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

