Regulatory T cell infiltration predicts outcome following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases
- PMID: 23010736
- PMCID: PMC3740360
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2668-9
Regulatory T cell infiltration predicts outcome following resection of colorectal cancer liver metastases
Abstract
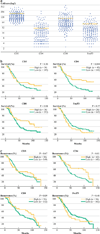
Background: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) counts in colorectal cancer liver metastases (CRCLM) predict survival following resection. While CD4 and CD8 T cells have been correlated with outcome following CRCLM resection, the role of regulatory T cells (Treg) is not well defined.
Methods: TIL in 188 patients who underwent CRCLM resection between 1998 and 2000 were analyzed by immunohistochemistry using tissue microarrays. Correlation between TIL composition and outcome was determined while controlling for established prognostic factors. Total T cells (CD3), helper T cells (CD4), cytotoxic T cells (CD8), and Treg (FoxP3) were analyzed.
Results: Median follow-up time was 40 months for all patients and 95 months for survivors. Overall survival (OS) at 5 and 10 years was 40 and 25%, respectively. The CD4 T cell count correlated with OS (p = .02) and recurrence-free survival (p = .04). A high number of CD8 T cells relative to total T cells (CD8:CD3 ratio) predicted longer OS times (p = .05). Analysis of Treg revealed that high FoxP3:CD4 (p = .03) and FoxP3:CD8 (p = .05) ratios were independent predictors of shorter OS. Patients with a high clinical risk score (CRS) were more likely to have a high number of intratumoral Treg, and patients ≥65 years old had a less robust CRCLM T cell infiltration.
Conclusions: A high number of Treg relative to CD4 or CD8 T cells predicted poor outcome, suggesting an immunosuppressive role for FoxP3 + TIL. The intratumoral immune response was an independent predictor of outcome in patients with colorectal liver metastases.
Figures


References
-
- Clemente CG, Mihm MC, Jr., Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Collini P, Cascinelli N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer. 1996;77:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B, et al. Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2328–2339. - PubMed
-
- Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pagés C, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–1964. - PubMed
-
- Pages F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, et al. Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med. 2005;353:2654–2666. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G, et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. New Engl J Med. 2003;348:203–213. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

