Small-molecule structure correctors target abnormal protein structure and function: structure corrector rescue of apolipoprotein E4-associated neuropathology
- PMID: 23013167
- PMCID: PMC4904786
- DOI: 10.1021/jm3008618
Small-molecule structure correctors target abnormal protein structure and function: structure corrector rescue of apolipoprotein E4-associated neuropathology
Abstract
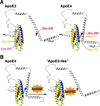
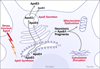
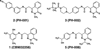
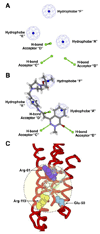
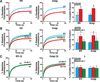
An attractive strategy to treat proteinopathies (diseases caused by malformed or misfolded proteins) is to restore protein function by inducing proper three-dimensional structure. We hypothesized that this approach would be effective in reversing the detrimental effects of apolipoprotein (apo) E4, the major allele that significantly increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. ApoE4's detrimental effects result from its altered protein conformation ("domain interaction"), making it highly susceptible to proteolytic cleavage and the generation of neurotoxic fragments. Here, we review apoE structure and function and how apoE4 causes neurotoxicity, and describe the identification of potent small-molecule-based "structure correctors" that induce proper apoE4 folding. SAR studies identified a series of small molecules that significantly reduced apoE4's neurotoxic effects in cultured neurons and a series that reduced apoE4 fragment levels in vivo, providing proof-of-concept for our approach. Structure-corrector-based therapies could prove to be highly effective for the treatment of many protein-misfolding diseases.
Figures

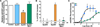
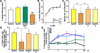
References
-
- Riordan JR. CFTR function and prospects for therapy. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008;77:701–726. - PubMed
-
- Van Goor F, Straley KS, Cao D, González J, Hadida S, Hazlewood A, Joubran J, Knapp T, Makings LR, Miller M, Neuberger T, Olson E, Panchenko V, Rader J, Singh A, Stack JH, Tung R, Grootenhuis PDJ, Negulescu P. Rescue of ΔF508-CFTR trafficking and gating in human cystic fibrosis airway primary cultures by small molecules. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006;290:L1117–L1130. - PubMed
-
- Pedemonte N, Tomati V, Sondo E, Galietta LJV. Influence of cell background on pharmacological rescue of mutant CFTR. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010;298:C866–C874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

