Is the C-terminal insertional signal in Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane proteins species-specific or not?
- PMID: 23013516
- PMCID: PMC3582582
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-510
Is the C-terminal insertional signal in Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane proteins species-specific or not?
Abstract
Background: In Gram-negative bacteria, the outer membrane is composed of an asymmetric lipid bilayer of phopspholipids and lipopolysaccharides, and the transmembrane proteins that reside in this membrane are almost exclusively β-barrel proteins. These proteins are inserted into the membrane by a highly conserved and essential machinery, the BAM complex. It recognizes its substrates, unfolded outer membrane proteins (OMPs), through a C-terminal motif that has been speculated to be species-specific, based on theoretical and experimental results from only two species, Escherichia coli and Neisseria meningitidis, where it was shown on the basis of individual sequences and motifs that OMPs from the one cannot easily be over expressed in the other, unless the C-terminal motif was adapted. In order to determine whether this species specificity is a general phenomenon, we undertook a large-scale bioinformatics study on all predicted OMPs from 437 fully sequenced proteobacterial strains.
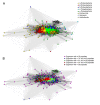
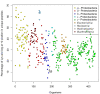
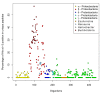
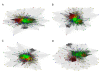
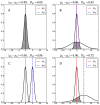
Results: We were able to verify the incompatibility reported between Escherichia coli and Neisseria meningitidis, using clustering techniques based on the pairwise Hellinger distance between sequence spaces for the C-terminal motifs of individual organisms. We noticed that the amino acid position reported to be responsible for this incompatibility between Escherichia coli and Neisseria meningitidis does not play a major role for determining species specificity of OMP recognition by the BAM complex. Instead, we found that the signal is more diffuse, and that for most organism pairs, the difference between the signals is hard to detect. Notable exceptions are the Neisseriales, and Helicobacter spp. For both of these organism groups, we describe the specific sequence requirements that are at the basis of the observed difference.
Conclusions: Based on the finding that the differences between the recognition motifs of almost all organisms are small, we assume that heterologous overexpression of almost all OMPs should be feasible in E. coli and other Gram-negative bacterial model organisms. This is relevant especially for biotechnology applications, where recombinant OMPs are used e.g. for the development of vaccines. For the species in which the motif is significantly different, we identify the residues mainly responsible for this difference that can now be changed in heterologous expression experiments to yield functional proteins.
Figures
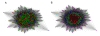




Similar articles
-
Species-specificity of the BamA component of the bacterial outer membrane protein-assembly machinery.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e85799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085799. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376896 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved lipid-facing basic residues promote the insertion of the porin OmpC into the E. coli outer membrane.mBio. 2025 Mar 12;16(3):e0331924. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03319-24. Epub 2025 Feb 20. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39976443 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of the BamBCDE Lipoproteins Revealed by Bypass Mutations in BamA.J Bacteriol. 2020 Oct 8;202(21):e00401-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00401-20. Print 2020 Oct 8. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32817097 Free PMC article.
-
Outer membrane biogenesis in Escherichia coli, Neisseria meningitidis, and Helicobacter pylori: paradigm deviations in H. pylori.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Apr 11;2:29. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00029. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Chaperones to the Membrane with a BAM!Trends Biochem Sci. 2016 Oct;41(10):872-882. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Trends Biochem Sci. 2016. PMID: 27450425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the lipid bilayer in outer membrane protein folding in Gram-negative bacteria.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 24;295(30):10340-10367. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011473. Epub 2020 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32499369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of Lewis b binding and sequence variation of the babA adhesin gene during chronic Helicobacter pylori infection in humans.mBio. 2014 Dec 16;5(6):e02281-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02281-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25516619 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Display of Chlamydia trachomatis PmpD Passenger at the Surface of Salmonella OMVs.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;13(4):366. doi: 10.3390/membranes13040366. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37103793 Free PMC article.
-
Outer membrane protein biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Oct 5;370(1679):20150023. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0023. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26370935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outer membrane protein evolution.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Jun;68:122-128. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 33493965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

