Guiding the design of synthetic DNA-binding molecules with massively parallel sequencing
- PMID: 23013524
- PMCID: PMC3483022
- DOI: 10.1021/ja308888c
Guiding the design of synthetic DNA-binding molecules with massively parallel sequencing
Abstract
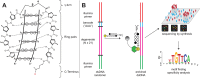
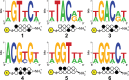
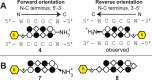
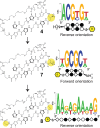
Genomic applications of DNA-binding molecules require an unbiased knowledge of their high affinity sites. We report the high-throughput analysis of pyrrole-imidazole polyamide DNA-binding specificity in a 10(12)-member DNA sequence library using affinity purification coupled with massively parallel sequencing. We find that even within this broad context, the canonical pairing rules are remarkably predictive of polyamide DNA-binding specificity. However, this approach also allows identification of unanticipated high affinity DNA-binding sites in the reverse orientation for polyamides containing β/Im pairs. These insights allow the redesign of hairpin polyamides with different turn units capable of distinguishing 5'-WCGCGW-3' from 5'-WGCGCW-3'. Overall, this study displays the power of high-throughput methods to aid the optimal targeting of sequence-specific minor groove binding molecules, an essential underpinning for biological and nanotechnological applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
On the pairing rules for recognition in the minor groove of DNA by pyrrole-imidazole polyamides.Chem Biol. 1997 Aug;4(8):569-78. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(97)90243-x. Chem Biol. 1997. PMID: 9281524
-
Binding of hairpin pyrrole and imidazole polyamides to DNA: relationship between torsion angle and association rate constants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11510-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks897. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23042247 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation sequencing studies guide the design of pyrrole-imidazole polyamides with improved binding specificity by the addition of β-alanine.Chembiochem. 2014 Dec 15;15(18):2647-51. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201402497. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 25371287
-
Sequence-specific DNA binding Pyrrole-imidazole polyamides and their applications.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 1;26(8):1393-1411. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.01.026. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29439914 Review.
-
Targeting the minor groove of DNA.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997 Jun;7(3):355-61. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(97)80051-6. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1997. PMID: 9204277 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the genomic targets of alkylating polyamide conjugates using high-throughput sequencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 May 19;44(9):4014-24. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw283. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27098039 Free PMC article.
-
Threading polyintercalators with extremely slow dissociation rates and extended DNA binding sites.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Aug 28;135(34):12783-9. doi: 10.1021/ja4057344. Epub 2013 Aug 20. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23919778 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of two large antiviral polyamides with the long control region of HPV16.Biochimie. 2016 Aug;127:103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.04.022. Epub 2016 May 4. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 27155361 Free PMC article.
-
Site-Specific Arrangement and Structure Determination of Minor Groove Binding Molecules in Self-Assembled Three-Dimensional DNA Crystals.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Dec 6;145(48):26075-26085. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c07802. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37987645 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem trimer pyrrole-imidazole polyamide probes targeting 18 base pairs in human telomere sequences.Chem Sci. 2015 Apr 1;6(4):2307-2312. doi: 10.1039/c4sc03755c. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29308145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dervan P. B.; Edelson B. S. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 284–99. - PubMed
-
- Wade W. S.; Mrksich M. L.; Dervan P. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8783–94.
-
- White S.; Szewczyk J. W.; Turner J. M.; Baird E. E.; Dervan P. B. Nature 1998, 391, 468–71. - PubMed
-
- White S.; Baird E. E.; Dervan P. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8756–65.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

