Species differences in somatodendritic dopamine transmission determine D2-autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of ventral tegmental area neuron firing
- PMID: 23015441
- PMCID: PMC3538874
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2745-12.2012
Species differences in somatodendritic dopamine transmission determine D2-autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of ventral tegmental area neuron firing
Abstract
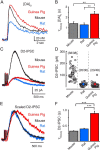
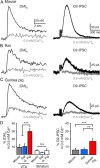
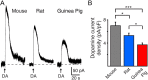
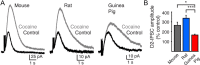
The somatodendritic release of dopamine within the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra pars compacta activates inhibitory postsynaptic D2-receptors on dopaminergic neurons. The proposed mechanisms that regulate this form of transmission differ between electrochemical studies using rats and guinea pigs and electrophysiological studies using mice. This study examines the release and resulting dopamine D2-autoreceptor-mediated IPSCs (D2-IPSCs) in the VTA of mouse, rat, and guinea pig. Robust D2-IPSCs were observed in all recordings from neurons in slices taken from mouse, whereas D2-IPSCs in rat and guinea pig were observed less frequently and were significantly smaller in amplitude. In slices taken from guinea pig, dopamine release was more persistent under conditions of reduced extracellular calcium. The decline in the concentration of dopamine was also prolonged and not as sensitive to inhibition of reuptake by cocaine. This resulted in an increased duration of D2-IPSCs in the guinea pig. Therefore, unlike the mouse or the rat, the time course of dopamine in the extracellular space of the guinea pig determined the duration the D2-IPSC. Functionally, differences in D2-IPSCs resulted in inhibition of dopamine neuron firing only in slices from mouse. The results suggest that the mechanisms and functional consequences of somatodendritic dopamine transmission in the VTA vary among species. This highlights the complexity that underlies dopamine-dependent transmission in one brain area. Differences in somatodendritic transmission would be expected in vivo to affect the downstream activity of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and subsequent terminal release.
Figures
References
-
- Aghajanian GK, Bunney BS. Dopamine“autoreceptors”: pharmacological characterization by microiontophoretic single cell recording studies. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977;297:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Barbour B, Keller BU, Llano I, Marty A. Prolonged presence of glutamate during excitatory synaptic transmission to cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994;12:1331–1343. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead MJ, Grandy DK, Wickman K, Williams JT. Vesicular dopamine release elicits an inhibitory postsynaptic current in midbrain dopamine neurons. Neuron. 2004;42:939–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
