Mitochondrial hyperfusion induced by loss of the fission protein Drp1 causes ATM-dependent G2/M arrest and aneuploidy through DNA replication stress
- PMID: 23015593
- PMCID: PMC4074216
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.109769
Mitochondrial hyperfusion induced by loss of the fission protein Drp1 causes ATM-dependent G2/M arrest and aneuploidy through DNA replication stress
Abstract
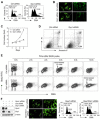
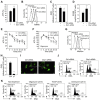
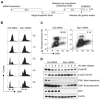
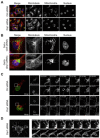
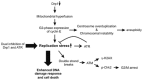
Mitochondrial fission and fusion cycles are integrated with cell cycle progression. In this paper, we demonstrate that the inhibition of mitochondrial fission protein Drp1 causes an unexpected delay in G2/M cell cycle progression and aneuploidy. In investigating the underlying molecular mechanism, we revealed that inhibiting Drp1 triggers replication stress, which is mediated by a hyperfused mitochondrial structure and unscheduled expression of cyclin E in the G2 phase. This persistent replication stress then induces an ATM-dependent activation of the G2 to M transition cell cycle checkpoint. Knockdown of ATR, an essential kinase in preventing replication stress, significantly enhanced DNA damage and cell death of Drp1-deficienct cells. Persistent mitochondrial hyperfusion also induces centrosomal overamplification and chromosomal instability, which are causes of aneuploidy. Analysis using cells depleted of mitochondrial DNA revealed that these events are not mediated by the defects in mitochondrial ATP production and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Thus dysfunctional mitochondrial fission directly induces genome instability by replication stress, which then initiates the DNA damage response. Our findings provide a novel mechanism that contributes to the cellular dysfunction and diseases associated with altered mitochondrial dynamics.
Figures


References
-
- Cassidy–Stone A., Chipuk J. E., Ingerman E., Song C., Yoo C., Kuwana T., Kurth M. J., Shaw J. T., Hinshaw J. E., Green D. R.et al. (2008). Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. Dev. Cell 14, 193–204 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.11.019 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

