Displacement of basolateral Bazooka/PAR-3 by regulated transport and dispersion during epithelial polarization in Drosophila
- PMID: 23015757
- PMCID: PMC3496619
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-09-0655
Displacement of basolateral Bazooka/PAR-3 by regulated transport and dispersion during epithelial polarization in Drosophila
Abstract
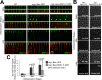
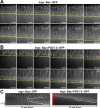
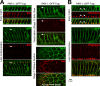
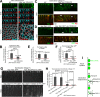
Polarity landmarks guide epithelial development. In the early Drosophila ectoderm, the scaffold protein Bazooka (Drosophila PAR-3) forms apicolateral landmarks to direct adherens junction assembly. However, it is unclear how Bazooka becomes polarized. We report two mechanisms acting in concert to displace Bazooka from the basolateral membrane. As cells form during cellularization, basally localized Bazooka undergoes basal-to-apical transport. Bazooka requires its three postsynaptic density 95, discs large, zonula occludens-1 (PDZ) domains to engage the transport mechanism, but with the PDZ domains deleted, basolateral displacement still occurs by gastrulation. Basolateral PAR-1 activity appears to act redundantly with the transport mechanism. Knockdown of PAR-1 sporadically destabilizes cellularization furrows, but basolateral displacement of Bazooka still occurs by gastrulation. In contrast, basolateral Bazooka displacement is blocked with disruption of both the transport mechanism and phosphorylation by PAR-1. Thus Bazooka is polarized through a combination of transport and PAR-1-induced dispersion from basolateral membranes. Our work complements recent findings in Caenorhabditis elegans and thus suggests the coupling of transport and dispersion is a common protein polarization strategy.
Figures
References
-
- Bayraktar J, Zygmunt D, Carthew RW. Par-1 kinase establishes cell polarity and functions in Notch signaling in the Drosophila embryo. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:711–721. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, St Johnston D. A conserved oligomerization domain in Drosophila Bazooka/PAR-3 is important for apical localization and epithelial polarity. Curr Biol. 2003a;13:1330–1334. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, St Johnston D. Drosophila PAR-1 and 14-3-3 inhibit Bazooka/PAR-3 to establish complementary cortical domains in polarized cells. Cell. 2003b;115:691–704. - PubMed
-
- Bohm H, Brinkmann V, Drab M, Henske A, Kurzchalia TV. Mammalian homologues of C. elegans PAR-1 are asymmetrically localized in epithelial cells and may influence their polarity. Curr Biol. 1997;7:603–606. - PubMed
-
- Doerflinger H, Benton R, Shulman JM, St Johnston D. The role of PAR-1 in regulating the polarised microtubule cytoskeleton in the Drosophila follicular epithelium. Development. 2003;130:3965–3975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

