Glycosides from marine sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): structures, taxonomical distribution, biological activities and biological roles
- PMID: 23015769
- PMCID: PMC3447334
- DOI: 10.3390/md10081671
Glycosides from marine sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae): structures, taxonomical distribution, biological activities and biological roles
Abstract
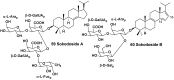
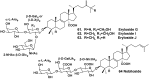
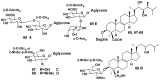
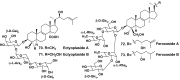
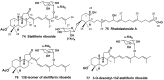
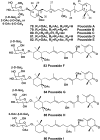
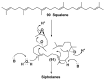
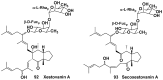
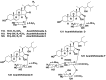
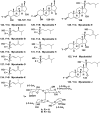
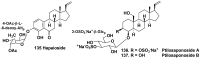
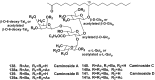
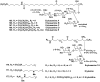
Literature data about glycosides from sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae) are reviewed. Structural diversity, biological activities, taxonomic distribution and biological functions of these natural products are discussed.
Keywords: activities; biological functions; glycosides; sponges; structures; taxonomic distribution.
Figures

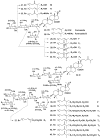
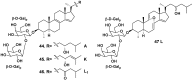
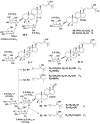
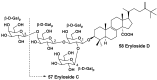

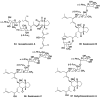
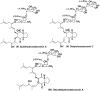
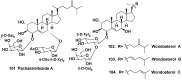
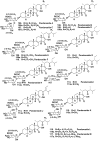

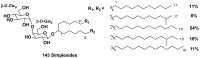

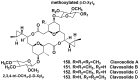
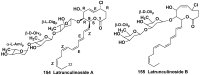
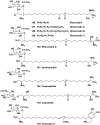
References
-
- Stonik V.A. Some terpenoid and steroid derivatives from echinoderms and sponges. Pure Appl. Chem. 1986;58:423–436. doi: 10.1351/paC198658030423. - DOI
-
- Stonik V.A., Kalinin V.I., Avilov S.A. Toxins from sea cucumbers (Holothuroids): Chemical structures, properties, taxonomic distribution, biosynthesis and evolution. J. Nat. Toxins. 1999;8:235–248. - PubMed
-
- Moraes G., Northcote P.T., Kalinin V.I., Avilov S.A., Silchenko A.S., Dmitrenok P.S., Stonik V.A., Levin V.S. Structure of the major triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Stichopus mollis and evidence to reclassify this species into the new genus Australostichopus. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2004;32:637–650. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2004.02.005. - DOI
-
- Avilov S.A., Kalinin V.I., Smirnov A.V. Use of triterpene glycosides for resolving taxonomic problems in the sea cucumber genus Cucumaria (Holothurioidea, Echinodermata) Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2004;32:715–733. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2003.12.008. - DOI
-
- Kalinin V.I., Silchenko A.S., Avilov S.A., Stonik V.A., Smirnov A.V. Sea cucumbers triterpene glycosides, the recent progress in structural elucidation and chemotaxonomy. Phytochem. Rev. 2005;4:221–236. doi: 10.1007/s11101-005-1354-y. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

