Rehabilitation of syndesmotic (high) ankle sprains
- PMID: 23015976
- PMCID: PMC3438867
- DOI: 10.1177/1941738110384573
Rehabilitation of syndesmotic (high) ankle sprains
Abstract
Context: High ankle sprains are common in athletes who play contact sports. Most high ankle sprains are treated nonsurgically with a rehabilitation program.
Evidence acquisition: All years of PUBMED, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, CINAHL PLUS, SPORTDiscuss, Google Scholar, and Web of Science were searched to August 2010, cross-referencing existing publications. Keywords included syndesmosis ankle sprain or high ankle sprain and the following terms: rehabilitation, treatment, cryotherapy, braces, orthosis, therapeutic modalities, joint mobilization, massage, pain, pain medications, TENS (ie, transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation), acupuncture, aquatic therapy, strength, neuromuscular training, perturbation training, and outcomes.
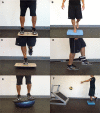
Results: Level of evidence, 5. A 3-phase rehabilitation program is described. The acute phase is directed at protecting the joint while minimizing pain, inflammation, muscle weakness, and loss of motion. Most patients are treated with some form of immobilization and have weightbearing restrictions. A range of therapeutic modalities are used to minimize pain and inflammation. Gentle mobilization and resistance exercises are used to gain mobility and maintain muscle size and strength. The subacute phase is directed at normalizing range of motion, strength, and function in activities of daily living. Progressive mobilization and strengthening are hallmarks of this phase. Neuromuscular training is begun and becomes the central component of rehabilitation. The advanced training phase focuses on preparing the patient for return to sports participation. Perturbation of support surfaces, agility drills, plyometrics, and sport-specific training are central components of this phase.
Conclusion: The rehabilitation guidelines discussed may assist clinicians in managing syndesmotic ankle sprains.
Keywords: ankle rehabilitation; distal tibiofibular sprain; syndesmosis ankle sprain; syndesmosis instability.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest declared.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso A, Khoury L, Adams R. Clinical tests for ankle syndesmosis injury: reliability and prediction of return to function. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1998;27(4):276-284 - PubMed
-
- Amendola A. Controversies in diagnosis and management of syndesmosis injuries of the ankle. Foot Ankle. 1992;13(1):44-50 - PubMed
-
- Bassett FH, 3rd, Gates HS, 3rd, Billys JB, Morris HB, Nikolaou PK. Talar impingement by the anteroinferior tibiofibular ligament: a cause of chronic pain in the ankle after inversion sprain. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72(1):55-59 - PubMed
-
- Beumer A. Chronic instability of the anterior syndesmosis of the ankle. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2007;78(327):4-36 - PubMed
-
- Beumer A, Valstar ER, Garling EH, et al. External rotation stress imaging in syndesmotic injuries of the ankle: comparison of lateral radiography and radiostereometry in a cadaveric model. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74(2):201-205 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

