Effect of patterned electrical neuromuscular stimulation on vertical jump in collegiate athletes
- PMID: 23016002
- PMCID: PMC3445136
- DOI: 10.1177/1941738110397871
Effect of patterned electrical neuromuscular stimulation on vertical jump in collegiate athletes
Abstract
Background: Patterned electrical neuromuscular stimulation (PENS) uses the electrical stimulation of sensory and motor nerves to achieve a skeletal muscle contraction using an electromyogram-derived functional pattern. PENS is used extensively for neuromuscular reeducation and treatment of muscle disuse atrophy.
Purpose: To explore the effectiveness of PENS as applied to the quadriceps muscles on the vertical jump of an athletic population.
Study design: Experimental with control and repeated measures over time.
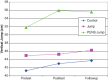
Methods: Healthy college athletes (54 women, 75 men) were divided into 3 groups (control, n = 30; jump, n = 33; and jump with PENS, n = 63). There was no difference among groups' height and weight. Athletes performed a baseline standing vertical jump using a vertical jump system. The control group continued its normal daily activities with no jumping tasks included. The jump groups performed 3 sets of 12 repetitions with a 2-minute rest between sets at a frequency of 3 times per week. The PENS group did the jumping with the coordination of an electrical stimulation system. Vertical jump was retested after 6 weeks of intervention and 2 weeks after cessation.
Results: A 3-way repeated measures analysis of variance for time (control, jump alone, jump with PENS) revealed a significant difference (P < 0.05) for time and an interaction between time and treatment, as well as a significant difference for the PENS group from baseline to posttest and for the jump group from posttest to follow-up jump. There was no significant difference between groups for the baseline vertical jump.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that 6 weeks of vertical jump training coordinated with PENS resulted in a greater increase than jumping only or control. This pattern of stimulation with PENS in combination with jump training may positively affect jumping.
Keywords: electrical stimulation; jumping; muscle reeducation; patterned stimulation.
Figures
References
-
- Andrews RJ. Neuroprotection Trek: the next generation, Neuromodulation II. Applications: epilepsy, nerve regeneration, neurotrophins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;993:14-24 - PubMed
-
- Bax L, Staes F, Verhagen A. Does neuromuscular electrical stimulation strengthen the quadriceps femoris? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sports Med. 2005;35(3):191-212 - PubMed
-
- Boutelle D, Smith B, Malone T. A strength study utilizing the Electro-Stim 180. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1985;7(2):50-53 - PubMed
-
- Caggiano E, Emery T, Shirley S, Craik RL. Effects of electrical stimulation on voluntary contraction for strengthening the quadriceps femoris muscles in aged male population. J Orthop Sports Physical Ther. 1994;20(1):22-28 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources