Patellofemoral disorders: role of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in defining abnormal rotational lower limb alignment
- PMID: 23016003
- PMCID: PMC3445137
- DOI: 10.1177/1941738111399372
Patellofemoral disorders: role of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in defining abnormal rotational lower limb alignment
Abstract
Background: The contribution of lower limb rotational malalignment to patellofemoral pain and instability has been well recognized. The purpose of the present study is to review the role of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in assessment of abnormal rotational alignment of lower limb.
Evidence acquisition: An analysis of all available literature in the English language through 2010 was performed to provide data on a comparison between MRI and CT-specifically, the techniques and normative values used to determine abnormal lower limb alignment.
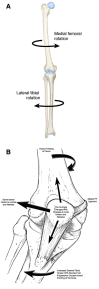
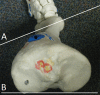
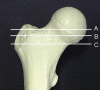
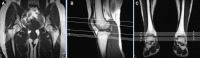
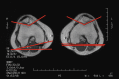
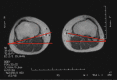
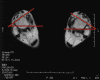
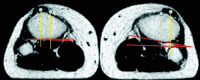
Results: CT and MRI are highly accurate in defining abnormal alignment of the lower limb. Determination of axis of femoral anteversion in proximal femur has been the subject of debate in the literature. The determination of distal femoral condylar axis, proximal tibial axis and distal tibial axis are less controversial.
Conclusions: CT and MRI are both used for assessing the rotational abnormalities of the femur and tibia during evaluation for patellofemoral disorders. MRI has an advantage over CT because femoral anteversion measurements are more accurate and ionizing radiation is avoided. A standardized protocol defining the level and axes for measurement of femoral and tibial alignment indices should be used to maintain consistency in measurements.
Keywords: computed tomography; femoral anteversion; magnetic resonance imaging; patellofemoral pain; tibial torsion.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest declared.
Figures








References
-
- Bauman PA, Singson R, Hamilton WG. Femoral neck anteversion in ballerinas. Clin Orthop. 1994;302:57-63 - PubMed
-
- Beaconsfield T, Pintore E, Maffulli N, Petri GJ. Radiological measurements in patellofemoral disorders: a review. Clin Orthop. 1994;308:18-28 - PubMed
-
- Billing L. Roentgen examination of the proximal femur end in children and adolescents: a standardized technique also suitable for determination of the collum, anteversion and epiphyseal angles. A study of slipped epiphysis and coxa plana. Acta Radiol. 1954;110(suppl):1 - PubMed
-
- Bruce WD, Stevens PM. Surgical correction of miserable malalignment syndrome. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(4):1-5 - PubMed
-
- Chung CY, Lee KM, Park S, et al. Validity and reliability of measuring femoral anteversion and neck-shaft angle in patients with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:1195-1205 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

