Regulators of innate immunity as novel targets for panviral therapeutics
- PMID: 23017246
- PMCID: PMC7102864
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2012.08.009
Regulators of innate immunity as novel targets for panviral therapeutics
Abstract
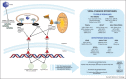
Interferons (IFNs) have long been used as an immunomodulatory therapy for a large array of acute and chronic viral infections. However, IFN therapies have been plagued by severe side effects. The discovery of pathogen recognition receptors (PRR) rejuvenated the interest for immunomodulatory therapies. The successes obtained with Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists in activating immune cells and as adjuvant for prophylactic vaccines against different viruses paved the way to targeted immunomodulatory therapy. Better characterization of pathogen-induced immune disorders and newly discovered regulators of innate immunity have now the potential to specifically withdraw prevailing subversion mechanisms and to transform antiviral treatments by introducing panviral therapeutics with less adverse effects than IFN therapies.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Takeuchi O., Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Hou F., Sun L., Zheng H., Skaug B., Jiang Q.X., Chen Z.J. MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response. Cell. 2011;146:448–461. - PMC - PubMed
-
Describes how viral infection induces the formation of prion-like aggregates of MAVS on mitochondria that potently activate IRF3.
-
- Kawai T., Akira S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity. 2011;34:637–650. - PubMed
-
- Eisenacher K., Krug A. Regulation of RLR-mediated innate immune signaling — it is all about keeping the balance. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012;91:36–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

