Unraveling oxyntomodulin, GLP1's enigmatic brother
- PMID: 23019069
- PMCID: PMC3493657
- DOI: 10.1530/JOE-12-0368
Unraveling oxyntomodulin, GLP1's enigmatic brother
Abstract
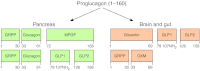
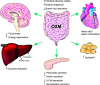
Oxyntomodulin (OXM) is a peptide secreted from the L cells of the gut following nutrient ingestion. OXM is a dual agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR) combining the effects of GLP1 and glucagon to act as a potentially more effective treatment for obesity than GLP1R agonists. Injections of OXM in humans cause a significant reduction in weight and appetite, as well as an increase in energy expenditure. Activation of GCGR is classically associated with an elevation in glucose levels, which would be deleterious in patients with T2DM, but the antidiabetic properties of GLP1R agonism would be expected to counteract this effect. Indeed, OXM administration improved glucose tolerance in diet-induced obese mice. Thus, dual agonists of the GCGR and GLP1R represent a new therapeutic approach for diabetes and obesity with the potential for enhanced weight loss and improvement in glycemic control beyond those of GLP1R agonists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon receptor dual agonism reverses obesity in mice.Diabetes. 2009 Oct;58(10):2258-66. doi: 10.2337/db09-0278. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Diabetes. 2009. PMID: 19602537 Free PMC article.
-
The glucagon receptor is involved in mediating the body weight-lowering effects of oxyntomodulin.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012 Aug;20(8):1566-71. doi: 10.1038/oby.2012.67. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2012. PMID: 22421924 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of oxyntomodulin and GLP-1 on glucose metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul 15;303(2):E265-71. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00142.2012. Epub 2012 May 22. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22621866
-
Action and therapeutic potential of oxyntomodulin.Mol Metab. 2013 Dec 14;3(3):241-51. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.12.001. eCollection 2014 Jun. Mol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24749050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of oxyntomodulin-based glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon co-agonist analogs in diabetes and obesity.Peptides. 2023 Apr;162:170955. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2023.170955. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Peptides. 2023. PMID: 36669563 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-, Delta- and PP-cells: Are They the Architectural Cornerstones of Islet Structure and Co-ordination?J Histochem Cytochem. 2015 Aug;63(8):575-91. doi: 10.1369/0022155415583535. J Histochem Cytochem. 2015. PMID: 26216135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the Brain a Key Player in Glucose Regulation and Development of Type 2 Diabetes?Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 26;10:457. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00457. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31133864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Class B1 GPCRs: insights into multireceptor pharmacology for the treatment of metabolic disease.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Nov 1;327(5):E600-E615. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00371.2023. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38984948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Pharmaceutical Design: Unleashing the Potential of Novel Therapeutics.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(16):2060-2077. doi: 10.2174/0113892010275850240102105033. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38288793 Review.
-
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Multi-Target Drugs.Molecules. 2020 Apr 23;25(8):1987. doi: 10.3390/molecules25081987. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32340373 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

