Determining how defects in connexin43 cause skeletal disease
- PMID: 23019186
- PMCID: PMC4540067
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.22349
Determining how defects in connexin43 cause skeletal disease
Abstract
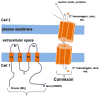
Gap junction channels mediate direct cell-cell communication via the exchange of second messengers, ions, and metabolites from one cell to another. Mutations in several human connexin (cx) genes, the subunits of gap junction channels, disturb the development and function of multiple tissues/organs. In particular, appropriate function of Cx43 is required for skeletal development in all vertebrate model organisms. Importantly, it remains largely unclear how disruption of gap junctional intercellular communication causes developmental defects. Two groups have taken distinct approaches toward defining the tangible molecular changes occurring downstream of Cx43-based gap junctional communication. Here, these strategies for determining how Cx43 modulates downstream events relevant to skeletal morphogenesis were reviewed.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Akimenko MA, Mari-Beffa M, Becerra J, Geraudie J. Old questions, new tools, and some answers to the mystery of fin regeneration. Dev Dyn. 2003;226:190–201. - PubMed
-
- Chung DJ, Castro CH, Watkins M, Stains JP, Chung MY, Szejnfeld VL, Willecke K, Theis M, Civitelli R. Low peak bone mass and attenuated anabolic response to parathyroid hormone in mice with an osteoblast-specific deletion of connexin43. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:4187–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

