Kisspeptin prevention of amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in vitro
- PMID: 23019497
- PMCID: PMC3447396
- DOI: 10.1021/cn300045d
Kisspeptin prevention of amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in vitro
Abstract
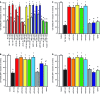
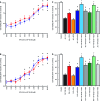
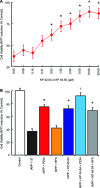
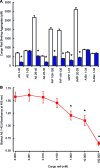
Alzheimer's disease (AD) onset is associated with changes in hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) function. The 54 amino acid kisspeptin (KP) peptide regulates the HPG axis and alters antioxidant enzyme expression. The Alzheimer's amyloid-β (Aβ) is neurotoxic, and this action can be prevented by the antioxidant enzyme catalase. Here, we examined the effects of KP peptides on the neurotoxicity of Aβ, prion protein (PrP), and amylin (IAPP) peptides. The Aβ, PrP, and IAPP peptides stimulated the release of KP and KP 45-54. The KP peptides inhibited the neurotoxicity of Aβ, PrP, and IAPP peptides, via an action that could not be blocked by kisspeptin-receptor (GPR-54) or neuropeptide FF (NPFF) receptor antagonists. Knockdown of KiSS-1 gene, which encodes the KP peptides, in human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells with siRNA enhanced the toxicity of amyloid peptides, while KiSS-1 overexpression was neuroprotective. A comparison of the catalase and KP sequences identified a similarity between KP residues 42-51 and the region of catalase that binds Aβ. The KP peptides containing residues 45-50 bound Aβ, PrP, and IAPP, inhibited Congo red binding, and were neuroprotective. These results suggest that KP peptides are neuroprotective against Aβ, IAPP, and PrP peptides via a receptor independent action involving direct binding to the amyloid peptides.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Benzothiazole aniline tetra(ethylene glycol) and 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole inhibit neuroprotection against amyloid peptides by catalase overexpression in vitro.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Nov 20;4(11):1501-12. doi: 10.1021/cn400146a. Epub 2013 Sep 9. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23968537 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Neurotransmitters in Protection against Amyloid- β Toxicity by KiSS-1 Overexpression in SH-SY5Y Neurons.ISRN Neurosci. 2013 Jul 17;2013:253210. doi: 10.1155/2013/253210. eCollection 2013. ISRN Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24967306 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-amyloid neurotoxicity requires fibril formation and is inhibited by congo red.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12243-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12243. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7991613 Free PMC article.
-
Fucosterol exerts protection against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity, reduces intracellular levels of amyloid β and enhances the mRNA expression of neuroglobin in amyloid β-induced SH-SY5Y cells.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jan;121:207-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.021. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30300695
-
Antagonism of neuronal prostaglandin E(2) receptor subtype 1 mitigates amyloid β neurotoxicity in vitro.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;8(1):87-93. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9380-1. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22718277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kisspeptin-13 Improves Spatial Memory Consolidation and Retrieval against Amyloid-β Pathology.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Fall;18(Suppl1):169-181. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.112199.13599. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32802097 Free PMC article.
-
Kisspeptin-10 Rescues Cholinergic Differentiated SHSY-5Y Cells from α-Synuclein-Induced Toxicity In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 6;23(9):5193. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095193. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563582 Free PMC article.
-
Immunolocalization of Kisspeptin Associated with Amyloid-β Deposits in the Pons of an Alzheimer's Disease Patient.J Neurodegener Dis. 2013;2013:879710. doi: 10.1155/2013/879710. Epub 2013 May 16. J Neurodegener Dis. 2013. PMID: 26317001 Free PMC article.
-
The Aggravating Role of Failing Neuropeptide Networks in the Development of Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 5;25(23):13086. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313086. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kisspeptin-54 attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats via GPR54/ARRB2/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Aug 1;171:99-111. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.05.012. Epub 2021 May 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33989759 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao A.-M.; Meynen G.; Swaab D. F. (2008) The stress system in depression and neurodegeneration: focus on the human hypothalamus. Brain Res. Rev. 57, 531–553. - PubMed
-
- Tortosa-Martínez J.; Clow A. (2012) Does physical activity reduce risk for Alzheimer’s disease through interaction with the stress neuroendocrine system?. Stress 15, 243–261. - PubMed
-
- Verdile G.; Yeap B. B.; Clarnette R. M.; Dhaliwal S.; Burkhardt M. S.; Chubb S. A. P.; de Ruyck K.; Rodrigues M.; Mehta P. D.; Foster J. K.; Bruce D. G.; Martins R. N. (2008) Luteinizing hormone levels are positively correlated with plasma amyloid-beta protein levels in elderly men. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 14, 201–208. - PubMed
-
- George J. T.; Millar R. P.; Anderson R. A. (2010) Hypothesis: kisspeptin mediates male hypogonadism in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Neuroendocrinology 91, 302–307. - PubMed
-
- Navarro V. M.; Tena-Sempere M. (2012) Neuroendocrine control by kisspeptins: role in metabolic regulation of fertility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 8, 40–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

