Amniotic fluid and maternal race influence responsiveness of fetal membranes to bacteria
- PMID: 23021257
- PMCID: PMC3596009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jri.2012.07.006
Amniotic fluid and maternal race influence responsiveness of fetal membranes to bacteria
Abstract
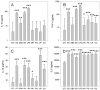
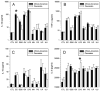
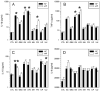
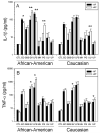
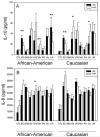
Spontaneous preterm birth (PTB) and preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (pPROM) occur more frequently in African-American women than in other racial groups. This may be due to an enhanced inflammatory response to pathogens associated with the condition. It is also possible that amniotic fluid (AF) has different immunomodulatory properties in African-American women that increase their risk of PTB and pPROM. To test this, we cultured fetal membranes from European-American and African-American women with sterile medium (control), Escherichia coli, Gardnerella vaginalis, Group B streptococci (GBS), Polyporphorans gingivalis, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum or Ureaplasma parvum in the presence and absence of 50% autologous AF. Cytokine concentrations were quantified in the conditioned medium. All bacterial species increased IL-8 production. IL-1β and TNF-α production were stimulated by LPS, E. coli, and G. vaginalis compared with control, but responses to Group B streptococci and P. gingivalis were limited to IL-1β and TNF-α respectively. Genital mycoplasmas stimulated TNF-α and IL-10 but had no effect on IL-1β production. African-Americans had twice the IL-1β response to E. coli as European-Americans (P=0.031). Conversely, European-Americans produced more IL-8 in response to LPS than African-Americans (P=0.026). AF had both pro- and anti-inflammatory properties that varied between races and pathogens. These results suggest that the host response to fetal membrane infections is complex and not generalizable. Interventions to prevent PTB and pPROM may need to be customized based on a patient's race, type of bacterial infection and factors in her AF.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Belanger M, Reyes L, von Deneen K, Reinhard MK, Progulske-Fox A, Brown MB. Colonization of maternal and fetal tissues by Porphyromonas gingivalisis strain dependent in a rodent animal model. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008;199:86.e1–86.e7. - PubMed
-
- Boggess KA, Madianos PN, Preisser JS, Moise KJ, Offenbacher S. Chronic maternal and fetal Porphyromonas gingivalis exposure during pregnancy in rabbits. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005a;192:554–557. - PubMed
-
- Boggess KA, Price WA, Preisser JS, Moise KJ, Offenbacher S. Insulin-like growth factor and interleukin-1beta levels and subsequent fetal size in response to chronic Porphyromonas gingivalis exposure in the pregnant rabbit. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005b;193:1219–1223. - PubMed
-
- Espinoza J, Chaiworapongsa T, Romero R, Gomez R, Kim JC, Yoshimatsu J, Edwin S, Rathnasabapathy C, Yoon BH. Evidence of participation of soluble CD14 in the host response to microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity and intra-amniotic inflammation in term and preterm gestations. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2002;12:304–312. - PubMed
-
- Etlinger HM, Chiller JM. Suppression of immunological activities by mouse amniotic fluid. Scand. J. Immunol. 1977;6:1241–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

