Ubiquinol decreases monocytic expression and DNA methylation of the pro-inflammatory chemokine ligand 2 gene in humans
- PMID: 23021568
- PMCID: PMC3542089
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-540
Ubiquinol decreases monocytic expression and DNA methylation of the pro-inflammatory chemokine ligand 2 gene in humans
Abstract
Background: Coenzyme Q₁₀ is an essential cofactor in the respiratory chain and serves in its reduced form, ubiquinol, as a potent antioxidant. Studies in vitro and in vivo provide evidence that ubiquinol reduces inflammatory processes via gene expression. Here we investigate the putative link between expression and DNA methylation of ubiquinol sensitive genes in monocytes obtained from human volunteers supplemented with 150 mg/ day ubiquinol for 14 days.
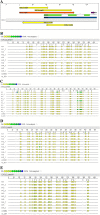
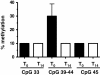
Findings: Ubiquinol decreases the expression of the pro-inflammatory chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 gene (CXCL2) more than 10-fold. Bisulfite-/ MALDI-TOF-based analysis of regulatory regions of the CXCL2 gene identified six adjacent CpG islands which showed a 3.4-fold decrease of methylation status after ubiquinol supplementation. This effect seems to be rather gene specific, because ubiquinol reduced the expression of two other pro-inflammatory genes (PMAIP1, MMD) without changing the methylation pattern of the respective gene.
Conclusion: In conclusion, ubiquinol decreases monocytic expression and DNA methylation of the pro-inflammatory CXCL2 gene in humans. Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN26780329.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ubiquinol affects the expression of genes involved in PPARα signalling and lipid metabolism without changes in methylation of CpG promoter islands in the liver of mice.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012 Mar;50(2):119-26. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-19. Epub 2011 Nov 11. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22448092 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ubiquinol-10 on microRNA-146a expression in vitro and in vivo.Mediators Inflamm. 2009;2009:415437. doi: 10.1155/2009/415437. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Mediators Inflamm. 2009. PMID: 19390647 Free PMC article.
-
The reduced form of coenzyme Q10 decreases the expression of lipopolysaccharide-sensitive genes in human THP-1 cells.J Med Food. 2011 Apr;14(4):391-7. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.0080. Epub 2011 Mar 3. J Med Food. 2011. PMID: 21370964
-
Micronutrient special issue: coenzyme Q(10) requirements for DNA damage prevention.Mutat Res. 2012 May 1;733(1-2):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.09.004. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 21964355 Review.
-
[Modern methodical approaches to determining the DNA methylation status and their use in oncology].Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2008 Jul-Aug;80(4):5-15. Ukr Biokhim Zh (1999). 2008. PMID: 19140445 Review. Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
Coenzyme Q regulates the expression of essential genes of the pathogen- and xenobiotic-associated defense pathway in C. elegans.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015 Nov;57(3):171-7. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.15-46. Epub 2015 Aug 29. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26566301 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial memory of early life stress and inflammation: Susceptibility to neurodegeneration in adulthood.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Oct;117:232-242. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.10.013. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 31703966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Combination of Physical Exercise with Muscle-Directed Antioxidants to Counteract Sarcopenia: A Biomedical Rationale for Pleiotropic Treatment with Creatine and Coenzyme Q10.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7083049. doi: 10.1155/2017/7083049. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29123615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mukai K, Itoh S, Morimoto H. Stopped-flow kinetic study of vitamin E regeneration reaction with biological hydroquinones (reduced forms of ubiquinone, vitamin K, and tocopherolquinone) in solution. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(31):22277–22281. - PubMed
-
- Crane FL, Navas P. The diversity of coenzyme Q function. Mol Aspects Med. 1997;18(Suppl):S1–S6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

