A TRPC6-dependent pathway for myofibroblast transdifferentiation and wound healing in vivo
- PMID: 23022034
- PMCID: PMC3505601
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.08.017
A TRPC6-dependent pathway for myofibroblast transdifferentiation and wound healing in vivo
Abstract
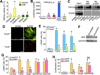
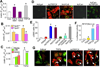
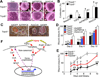
After injury or cytokine stimulation, fibroblasts transdifferentiate into myofibroblasts, contractile cells that secrete extracellular matrix for wound healing and tissue remodeling. Here, a genome-wide screen identified TRPC6, a Ca(2+) channel necessary and sufficient for myofibroblast transformation. TRPC6 overexpression fully activated myofibroblast transformation, while fibroblasts lacking Trpc6 were refractory to transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and angiotensin II-induced transdifferentiation. Trpc6 gene-deleted mice showed impaired dermal and cardiac wound healing after injury. The profibrotic ligands TGF-β and angiotensin II induced TRPC6 expression through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) serum response factor (SRF) signaling via the TRPC6 promoter. Once induced, TRPC6 activates the Ca(2+)-responsive protein phosphatase calcineurin, which itself induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation. Moreover, inhibition of calcineurin prevented TRPC6-dependent transdifferentiation and dermal wound healing. These results demonstrate an obligate function for TRPC6 and calcineurin in promoting myofibroblast differentiation, suggesting a comprehensive pathway for myofibroblast formation in conjunction with TGF-β, p38 MAPK, and SRF.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
A TRP to cardiac fibroblast differentiation.Channels (Austin). 2013 May-Jun;7(3):211-4. doi: 10.4161/chan.24328. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Channels (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23511028 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

