Cripto-1 enhances the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by binding to LRP5 and LRP6 co-receptors
- PMID: 23022962
- PMCID: PMC3508164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.09.024
Cripto-1 enhances the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by binding to LRP5 and LRP6 co-receptors
Abstract
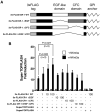
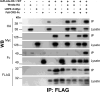
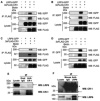
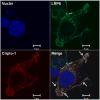
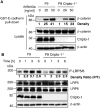
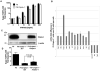
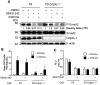
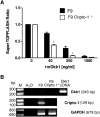
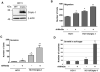
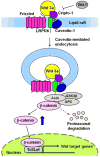
Cripto-1 is implicated in multiple cellular events, including cell proliferation, motility and angiogenesis, through the activation of an intricate network of signaling pathways. A crosstalk between Cripto-1 and the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been previously described. In fact, Cripto-1 is a downstream target gene of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the embryo and in colon cancer cells and T-cell factor (Tcf)/lymphoid enhancer factor binding sites have been identified in the promoter and the first intronic region of the mouse and human Cripto-1 genes. We now demonstrate that Cripto-1 modulates signaling through the canonical Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf pathway by binding to the Wnt co-receptors low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5 and LRP6, which facilitates Wnt3a binding to LRP5 and LRP6. Cripto-1 functionally enhances Wnt3a signaling through cytoplasmic stabilization of β-catenin and elevated β-catenin/Tcf transcriptional activation. Conversely, Wnt3a further increases Cripto-1 stimulation of migration, invasion and colony formation in soft agar of HC11 mouse mammary epithelial cells, indicating that Cripto-1 and the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling co-operate in regulating motility and in vitro transformation of mammary epithelial cells.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

