High-throughput, multiplexed IgG subclassing of antigen-specific antibodies from clinical samples
- PMID: 23023091
- PMCID: PMC3475184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2012.09.007
High-throughput, multiplexed IgG subclassing of antigen-specific antibodies from clinical samples
Abstract
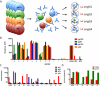
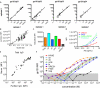
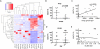
In vivo, the activity of antibodies relies critically on properties of both the variable domain, responsible for antigen recognition, and the constant domain, responsible for innate immune recognition. Here, we describe a flexible, microsphere-based array format for capturing information about both functional ends of disease-specific antibodies from complex, polyclonal clinical serum samples. Using minimal serum, we demonstrate IgG subclass profiling of multiple antibody specificities. We further capture and determine the subclass of epitope-specific antibodies. The data generated in this array provides a profile of the humoral immune response with multi-dimensional metrics regarding properties of both variable and constant IgG domains. Significantly, these properties are assessed simultaneously, and therefore information about the relationship between variable and constant domain characteristics is captured, and can be used to predict functions such as antibody effector activity.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Curtis KA, Kennedy MS, Charurat M, Nasidi A, Delaney K, Spira TJ, Owen SM. Development and characterization of a bead-based, multiplex assay for estimation of recent HIV type 1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2012;28:188–97. - PubMed
-
- Gomez-Roman VR, Florese RH, Patterson LJ, Peng B, Venzon D, Aldrich K, Robert-Guroff M. A simplified method for the rapid fluorometric assessment of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol Methods. 2006;308:53–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

