Upregulation of connexins 30 and 32 gap junctions in rat hippocampus at transcription level by chronic central injection of lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 23023213
- PMCID: PMC3629930
- DOI: 10.6091/ibj.1099.2012
Upregulation of connexins 30 and 32 gap junctions in rat hippocampus at transcription level by chronic central injection of lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
Background: Gap junctions composed of connexins (Cx) are functional in cell defense by propagation of toxic/death molecules to neighboring cells. Hippocampus, one of the brain regions with particular vulnerability to damage, has a wide network of gap junctions. Functional response of astrocytic Cx30 and neuronal Cx32 to hippocampal damage is unknown.
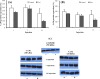
Methods: We infused lipopolysaccharide (LPS) intracerebroventricularly (2.5 mug/rat) once daily for two weeks to create neuroinflammation. The mRNA and protein levels of the Cx were measured in the hippocampus after 1st, 7th and 14th injection by real-time PCR and Western-blot techniques.
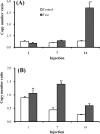
Results: A significant increase in Cx32 and Cx30 gene expression was observed after 7th and 14th injection of LPS with no significant change in their protein abundance.
Conclusion: Transcriptional overexpression of hippocampal Cx30 and Cx32 could be an adaptive response to production of intracellular toxic molecules but it is not accompanied with post- transcriptional overexpression and might have no functional impact.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of chronic intracerebroventricluar administration of lipopolysaccharide on connexin43 protein expression in rat hippocampus.Iran Biomed J. 2012;16(1):25-32. doi: 10.6091/ibj.1030.2012. Iran Biomed J. 2012. PMID: 22562029 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of connexin 30 and connexin 32 in hippocampus of rat during epileptogenesis in a kindling model of epilepsy.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Dec;28(6):729-36. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1279-6. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 23149765 Free PMC article.
-
Intracerebroventricular injection of lipopolysaccharide increases gene expression of connexin32 gap junction in rat hippocampus.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2013 Fall;4(4):334-40. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 25337366 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal expression of neuronal connexins during hippocampal ontogeny.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Apr;32(1):57-71. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00096-x. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000. PMID: 10751657 Review.
-
Diversity and molecular anatomy of gap junctions.Med Electron Microsc. 2001 Sep;34(3):153-9. doi: 10.1007/s007950100008. Med Electron Microsc. 2001. PMID: 11793189 Review.
Cited by
-
Panax Notoginseng Saponin Rg1 Can Effectively Improve the Cognitive Function of 5 × FAD Mice.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Apr 11;2022:5152761. doi: 10.1155/2022/5152761. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 16;2023:9823801. doi: 10.1155/2023/9823801. PMID: 35449867 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
PTEN Expression Regulates Gap Junction Connectivity in the Retina.Front Neuroanat. 2021 May 20;15:629244. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2021.629244. eCollection 2021. Front Neuroanat. 2021. PMID: 34093139 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Homer1b/c in neuronal apoptosis following LPS-induced neuroinflammation.Neurochem Res. 2015 Jan;40(1):204-15. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1460-6. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25503822
-
Nrdp1 is Associated with Neuronal Apoptosis in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation.Neurochem Res. 2015 May;40(5):971-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1552-y. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25896295
-
Connexins and their channels in inflammation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Nov/Dec;51(6):413-439. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2016.1204980. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27387655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Condorelli DF, Trovato-salinaro A, Mudo G, Mirone MB, Belluardo N. Cellular expression of connexins in the rat brain: neuronal localization, effects of kainate-induced seizures and expression in apoptotic neuronal cells. Euro J Neurosci. 2003 Oct;18(7):1807–27. - PubMed
-
- Söhl G, Maxeiner S, Willecke K. Expression and functions of neuronal gap junctions. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005 Mar;6(3):191–200. - PubMed
-
- Rouach N, Avignone E, Meme W, Koulakoff A, Venance L, Blomstrand F, et al. Gap junctions and connexin expression in the normal and pathological central nervous system. Biol Cell. 2002 Nov;94(7-8):457–75. - PubMed
-
- Froger N, Orellana JA, Cohen-Salmon M, Ezan P, Amigou E, Saez JC, et al. Cannabinoids prevent the opposite regulation of astroglial connexin43 hemichannels and gap junction channels induced by pro-inflammatory treatments. J Neurochem. 2009 Dec;111(6):1383–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
